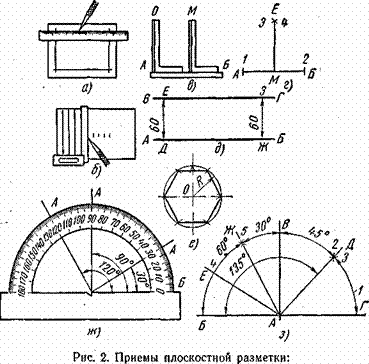
|
Slide 2
When stone work more often used brick. Three types of bricks are most known: Saman - from clay and filler; ceramic (clay, red) - from baked clay; silicate, consisting of sand and lime
Slide 3
Safety requirements before starting work 7. Before starting work, bricklayers are obliged to: a) present to the work manager a certificate of knowledge testing of safe working methods; b) wear a helmet, clothing, special-purpose shoes of the established sample; c) get a job to do the work of the team leader or work supervisor and undergo briefing at the workplace, taking into account the specifics of the work performed. After receiving the assignment from the team leader or work supervisor, the bricklayers are obliged to: a) prepare the necessary personal protective equipment, check their operability; b) check the workplace and its approaches for compliance with safety requirements; c) to prepare the technological equipment, the tool, necessary when performing the work, to check their compliance with the safety requirements.
Slide 4
At the workplace of a bricklayer should be located 1 - trays with a stone; 2 - a box with a solution; 3 - wall.
Slide 5
Safety requirements during operation When masonating buildings, bricklayers are required to: a) place brick and mortar on ceilings or scaffolding in such a way that a passage of at least 0.6 m wide remains between them and the building wall and that working flooring is not overloaded; b) use means of collective protection (fencing, catching devices) or a safety belt with a safety rope when laying walls to a height of up to 0.7 m from the working deck if the distance to the wall surface (floor) is more than 1.3 m; c) to build each subsequent floor of the building only after laying the ceilings above the erected floor; d) to close up the voids in the slabs before their submission to the masonry site to the design position. 11. Bricklayers are obliged to fasten the safety belt at the places indicated by the work supervisor when laying: a) cornices, parapets, as well as alignment of corners, facade cleaning, installation, disassembly and cleaning of protective visors; b) the walls of elevator shafts and other works performed near unprotected differences in height of 1.3 m and more; c) walls more than 0.75 m thick while standing on the wall. Before beginning to lay the outer walls, bricklayers should make sure that there are no people in the danger zone below, close to the place of work. When moving and feeding bricks, ceramic stones and small blocks to a workplace with cranes, pallets, containers and load handling devices should be used to prevent the load from falling. Bricklayers engaged in slinging cargo must have a certificate for slingers and comply with the requirements of instructions for slinging goods MI-3-10-2009. In order to avoid falling of the pallets moved by the crane, freed from the bricks, before slinging them it is necessary to tie them up in packages. When the crane moves the elements of prefabricated building structures (floor slabs, lintels, flight of stairs, platforms, and other products), bricklayers must be located outside the hazardous area caused by the movement of cranes. Approaching the specified elements is allowed only at a distance of no more than 0.5 m after they are lowered above the installation site in the design position. During the acceptance of elements of prefabricated building structures should not be between the received structural elements and the nearest edge of the outer wall. Elements of prefabricated building structures should be installed without jerks and blows on the mounted elements of building structures. When installing overlappings, it is necessary to lay out the solution with a spade with a long handle. The trowel should not be used for this purpose. When performing work on punching furrows, adjusting bricks and ceramic stones by chipping, masons are required to use safety glasses. When handing materials into pits or to underlying workplaces, masons are required to use inclined gutters with side boards. To accept the materials lowered along the chute, should be after their descent is stopped. Dropping materials from a height is not allowed. When working with solutions with chemical additives, bricklayers are required to use the protective equipment provided by the routing for the specified work.
In the process of building foundations and basement walls, it is necessary to check the quality of fixing the walls of trenches and trenches, and for convenience, it is advisable to leave a free space about 0.5 m wide between the lower edge of the trench or trench and the outer plane of the foundation or wall. In a trench or trench, workers must descend through stepladders fenced in with a railing. It is impossible to lower a stone on a trench with its simultaneous reception from a trench, it is also impossible to dump a stone in a ditch and a trench from a brow.
The height of each tier of the masonry is set so that the level of the masonry after each movement is not less than two rows of stone above the level of the scaffolds or floors. The masonry should be made only from interfloor overlappings and internal scaffoldings. It is forbidden to erect walls while standing on the Forests and scaffolding for masonry must meet the physical conditions and safety requirements. When building masonry in hazardous areas, bricklayers should use safety belts, attaching them to stable parts of the building or structure with their help. The laying of walls with a height of more than two floors should be made with a mandatory device of floors or temporary flooring of appropriate strength and rigidity, as well as staircases and platforms with fencing. At the workplace, stones in the form of packages, laid on pallets with cases excluding the possibility of their falling out, should be supplied with load-lifting mechanisms. All devices used for lifting materials must be provided with devices that prevent their spontaneous disclosure and material falling out. It is impossible to dump empty pallets, containers, boxes, cases, etc. from ceilings, scaffoldings and scaffoldings. They can be lowered only with the help of load-lifting mechanisms.
When laying walls from inside the building or structure, outside the entire perimeter of the building, install protective visors in the form of a 1.5 m wide flooring, laid on brackets at an angle of 20 ° to the horizontal surface and designed for the perception of a concentrated load of 1600 N applied in the middle of the span between the brackets .
From the outside, the visors are equipped with side boards. The brackets are hung on steel hooks, embedded in the masonry as it is erected at a distance of not more than 3 m from each other.
When erecting stone walls with a height of not more than 7 m, instead of installing visors, they can be installed on the ground around the perimeter of a building or structure at a distance of at least 1.5 m from the wall. In this case, above the entrances to a building or structure, canopies of at least 2X2 m are arranged in size.
It is forbidden to leave on the walls during the materials, debris, tools.

Articles similar to SAFETY AT STONE WORKS:
-
The foundation is a structure that takes the loads of structures and distributes them throughout their ...
-
Before the masonry is laid, quarrots of stones are prepared by the cleats, foundations for the mortar, ...
The most common causes of injury in the performance of stone work are: the absence of fences, falling from the height of materials and tools, the use of imperfect and unstable forests, scaffolding, step ladders, work without personal protective equipment.
When moving and feeding bricks, ceramic stones, blocks of tiles to the workplace with cranes, it is necessary to use pallets, containers, grabs and other devices that prevent the load from falling when lifting. When submitting bricks to the workplace in packages on pallets, it is necessary to use quadrilateral and triangular cases with an inclination towards the fenced rear wall of approximately 15%.
The solution should be supplied to the workplace with self-unloading buckets (into bunkers or mortar boxes) or with special containers (with four loops) with the help of load-lifting cranes.
The laying of walls is allowed from scaffolding, scaffolding or overlappings, and the height of each layer of the wall is taken so that the level of masonry after each movement of scaffolding is not less than 0.7 m above the level of the working floor or floor. If it is necessary to produce masonry below this level, the masonry should be carried out using safety belts or special mesh protective fences.
When the wall thickness is more than 0.75 m, it is allowed to make laying from the wall using a safety belt attached to a special safety device. Laying of external walls up to 0.75 m thick while standing on a wall is not allowed. The laying of the walls of buildings on the next floor without the installation of supporting structures for interfloor overlapping, as well as platforms and marches in the stairwells is not allowed.
Without protective visors, it is permitted to lay walls up to 7 m high and also more than 7 m high, subject to the use of mesh fences installed at the masonry level.
When laying walls with a height of more than 7 m, it is necessary to use protective visors around the perimeter of the building that meet the following requirements:
- the width of the visor should be at least 1.5 m, and they should be installed with a slope to the wall so that the angle formed between the lower part of the building wall and the surface of the visor is 110 °, and the gap between the building wall and the visor flooring is not exceeded 50 mm;
- protective peaks must withstand a uniformly distributed snow load established for a given climatic region and a concentrated load of at least 1600 N (160 kgf) applied in the middle of the span;
- the first row of protective visors should have a solid flooring at a height of not more than 6 m from the ground and be maintained until the completion of the masonry walls;
- the second row, made solid or from mesh materials with a cell of no more than 50 x 50 mm, should be installed at a height of 6–7 m above the first row, and then rearranged every 6–7 m along the laying.
Workers engaged in the installation, cleaning or removal of protective visors should work with safety belts. Walk on the visor, use them as scaffolding, and also put materials on them is not allowed.
When laying walls with internal scaffolding, external protective inventory canopies in the form of flooring on brackets or consoles manufactured from window openings should be arranged around the perimeter of the building, and canopies of 2 × 2 m in size should be mounted above the entrances to the staircase. Brackets should be hung on steel hooks, embedded in the masonry walls as it is erected and no more than 3 m apart from each other.
Laying walls with internal scaffoldings is allowed at a building height of no more than 7 m, but it is imperative to arrange a fence around the entire perimeter of the building at a distance of not less than 1.5 m from the wall, and above the entrances, in addition, you need to make 2 x awnings 2 m.
The most dangerous work in the production of stone work is laying eaves. The laying of the cornices of any profile, protruding from the planes of the walls by more than 30 cm, can be made only from outdoor forests. When laying brick eaves on final structures (reinforced concrete slabs, etc.) they are firmly fixed on anchors. The danger zone in places of masonry should be fenced, as the safety peaks are not designed to protect against the fall of concrete slabs from eaves.
When constructing eaves, it is prohibited to work or stand on the wall itself or below it under the place of laying. In the process of making the eaves, it is necessary to carefully monitor the strength of its elements and, above all, correct and reliable anchoring of the eaves and the balancing of its brickwork.
It is forbidden to stand or walk on the slab of the cornice and along the rail itself, as well as to lean on it the bars for hanging the cradles, as the curtain rail may collapse during testing of cradles or during work.
When installing wall cladding plates, which are usually performed from internal scaffolds simultaneously with masonry, workers should use safety belts.
It is possible to remove temporary fastenings of elements of the cornice or wall lining after the mortar reaches the strength established by the project.
It is allowed to interrupt the masonry, which is made simultaneously with the outer facing, only after laying the wall to the level of the upper edge of the facing slabs. The jointing of the exterior joints should be performed after laying out each row of scaffolding.
If the platforms and flights in the stairwells are not constructed or not fenced, or there is no interfloor overlap, or the belt flooring along the beams of these overlaps is not arranged, it is prohibited to lay walls to a height of more than two floors.
In the production of stone work special attention devote to the state of scaffolding and scaffolding and compliance with the rules of their operation.
1. The floorboards are laid stably, without gaps.
2. When laying boards at a height of more than 1.1 m, they arrange a fence, as a rule, an inventory with a height of at least 1 m.
3. To the bottom along the flooring, fix the side board with a height of at least 150 mm, and fix the handrail on top.
4. Metal scaffolding must be grounded.
5. Scaffolding and scaffolding cannot be overloaded with an excess stock of materials. 6. Nastil arrange two rows below the level of masonry and do not bring to the wall by 50mm.
7. Every day, at the end of the shift, the garbage is removed from the flooring, putting it in a box for feeding the crane to the ground in the allotted place.
8. Upon delivery of materials to the workplace, it is necessary to exclude their fall in the process of moving by a crane or along rolling steps. Prohibited dump free trays, grabs, crates, etc. from scaffolding and floors They are removed by crane.
Brickwork perform with ceilings or internal scaffolding (scaffolding), and to exclude injuries working around the perimeter of the building on the outside, install protective visors on metal brackets. Protective visors on the racks are also installed above the entrances to the building under construction. The first visor around the perimeter of the walls is set at a height of 6 m from the ground, and the next after 6… 7 m in height. Peaks cannot be used as scaffolding. They can not get up and store materials. To install and remove the visors should be full-time construction workers. On buildings up to 7 m high visors are not installed. In this case, on the ground at a distance of 1.5 m from the wall make a fence, for which no one from the workers can enter.
When performing masonry wallsincluding when jointing, it is forbidden to be on the wall. These processes are performed with scaffolding after laying each row of stones. Curtain rods protruding from the wall by more than 300mm are laid out from outdoor forests.
In the process construction of a building the ascent of the workers to the floors must be organized in a permanent staircase, along mounted flight stairs with permanent or temporary railings.
The source of injury can be a bad tool. Do not use a tool loosely seated on the handle. Working edges must be sharp, free of burrs. Tool should be used only for its intended purpose. It is necessary to constantly monitor the instrument, keep it clean and in a state of readiness for work.
It is desirable that the bricklayer be dressed in height-fitting workwear - overalls or a jacket with trousers. Do not remove clothing and headgear during work. In addition to direct injury, you can get a severe heat stroke. In order not to erase the skin on your hands with a stone and to exclude its corrosiveness with cement or lime mortar, you need to work in mittens or fingertips.
The possibility of injuring each other when working should be excluded the right

The economic part.
When calculating performance
workers use basic regulatory data:
Brick consumption per 1 m 3 of masonry is about 400,
A solution of 0.24 m 3;
Labor costs per 1 m 3 masonry from 0.77 to 2 people / day;
The average output per worker per shift 0,8 ... 1,1 m 3.
Actual performance per worker per shift:
working "loner" - 300 ... 500 pcs. brick or 0.7 ... 1.2 m 3 masonry;
worker in the level of "two" - about 1000 pcs. brick or 2.5 m 3;
in the “five” link - 1700 ... 2000 pcs. brick or 4.2 ... 5.0 m 3
We will find how many bricks and mortar are needed to complete the laying of piers with a thickness of 2 bricks to the height of a room 2.5 with a width of 3 m.
1. Determine the amount of masonry:
0, 51x3.00x2.5 = 3.825 cubic meters
2. Determine brick consumption
3.825х400 = 1530pcs.
3. Determine the flow rate of the solution
3.825х0.25 = 0.96 cubic meters
4. Labor costs
1.2x3.825 = 4.59 people \\ days.
Conclusion. For the performance of ornamental laying 2 bricks thick to the height of a room 2.5 with a width of 3 m, 1530 pieces are needed. ordinary clay bricks, 0.96 cubic meters of mortar. Labor costs are 4.59 man / day.


Conclusion
In our country, the issue of providing the population with housing is acute. This issue deals with the government at the highest levels of government. The primary task of the government is to provide housing for the population. In this regard, the state allocates huge funds for the construction of buildings and structures. The industry is also booming in Russia. And new economic zones are being built. Growing factories and enterprises.
At the moment, uses a variety of new technologies for construction. But still the main building materials is brick, for many centuries. This building material allows you to build both simple structures and buildings, as well as complex architectural structures. The brick is one of durable materials, and also simple in production and in use.
For the construction work requires many workers. To perform stone work requires specialists. On the construction sites of the country are many masons. From the bricklayer requires a variety of skills. He must strictly observe the technological sequence, be able to use various tools and devices, perform his work qualitatively.
Since ancient times, construction workers have been valued by the people. Hopefully, I knowingly chose this profession.

Literature
1. Kupriyanov, G.V. Mason: textbook for elementary vocational education / GVKupriyanov.- M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2012.-64s.
2. Kulikov, ON Labor protection in construction: a manual for elementary vocational education / О.N. Kulikov, E.I. Romin. - Moscow: Akademiya Publishing Center, 2013 - 416 p.
3. Lukin, A.A. The technology of stone work: a textbook for elementary vocational education / A.A. Lukin.- M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2013.-256 p.
4. Lukin A.A. The technology of stone work: a textbook for elementary vocational education / A.A. Lukin.- M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 2012.-256 p.
Internet resources:
1. cmet4uk.ru Typical flow charts
2. www.stroyplan.ru Typical routing for stone work
3. www.injene.ru Reference regulatory system
4. www.gost-snip-rd rf / Technological schemes and standard sets
5. snip1.ru/kladka-sten-iz-kirpica Building portal
6. www / buildinn.ru. Labor organization at construction sites and safety engineering
7. woodros.com Stone Works, I.I. Ishchenko
This labor protection instruction for the bricklayer is available for free viewing and downloading. The labor protection instruction for the bricklayer was prepared on the basis of the joint venture 12-135-2003 “Labor safety in construction. Industry standard instructions for labor protection "containing industry standard instruction on labor protection - TI PO 004-2003, taking into account the requirements of current legislative and regulatory acts containing state regulatory labor protection requirements specified in Appendix 1 and is intended for the bricklayer works according to the profession and qualifications. 1. GENERAL PROTECTION OF LABOR PROTECTION 1.1. As a bricklayer, persons aged under 18 years old who have passed a medical commission are allowed, as well as:
- introductory and primary briefings on labor protection;
- internship;
1.2. In the course of work, the bricklayer is affected by adverse meteorological conditions: rain, wind, low temperature, etc. Overalls contribute to a reduction in the negative influence of these factors.
1.3. The bricklayer is allowed to work if the following personal protective equipment is available: bib overalls; mittens combined, jacket and pants with insulated lining, felt boots
1.4. The bricklayer must comply with:
- internal regulations, especially regarding the prohibition of being at work in a state of alcoholic or drug intoxication;
- fire safety rules;
- rules of personal hygiene.
Undergo a periodic medical examination in accordance with the procedure established by the Ministry of Health and Social Development.
1.5. To be able to provide assistance to victims of injuries.
1.6. The following dangerous, harmful production factors can affect the work of a bricklayer:
- the location of the workplace at a height;
- driving machines and mechanisms;
- moving structures;
- collapsing structures;
- neuro-psychological stress;
- unstable constructions of scaffolding and scaffolding;
- increased dust and air pollution of the working area;
- sharp crumbs, burrs and roughness on the treated surface;
- increased voltage in the electrical circuit, the closure of which can occur through the body of the worker.
1.7. When traveling to the place of work and back by car, strictly follow the rules for transporting people in a car and follow the instructions of the senior on the car.
1.8. The following rules must be observed at the construction site:
a) be attentive to the signals given by crane operators and drivers of moving vehicles, and carry them out:
- not to be under the lifted load;
- pass only in the places intended for passage and marked with signs;
- be in a helmet;
- It is forbidden to use lifting mechanisms for lifting people;
- do not go beyond the fence of hazardous areas;
- places where work is performed at a height, bypass at a safe distance, since objects may fall from a height;
- in order to avoid eye disease, do not look at the flame of electric welding;
- do not touch electrical equipment and electrical wires (especially beware of bare or dangling drives); do not remove fences and protective covers from current-carrying equipment parts;
- do not eliminate electrical equipment malfunctions;
- do not work on the mechanisms without special training and admission;
- perform only the assigned work;
- do not use sanitary facilities for purposes other than intended (as an overnight stay, etc.);
- in case of an accident, immediately seek medical help and at the same time inform the master (foreman) about the incident;
- noticing violation of instructions by other workers or danger to others, do not remain indifferent, but warn the worker and foreman about the necessity of complying with the requirements ensuring the safety of work.
1.9. The worker should be aware that in case of violation of the requirements of the instructions, he is liable in accordance with applicable law. 2. REQUIREMENTS FOR LABOR PROTECTION BEFORE YOU BEGIN 2.1. To receive instructions from the master on safe methods, techniques and sequence of the production task, as well as on protective devices and scaffoldings intended for the performance of work, to familiarize yourself with the technological map of the operational installation of reinforced concrete structures and stone work.
2.2. Inspect the workplace and check the placement of materials.
2.3. Make sure that the inventory, tools, devices and devices that will have to be used during operation are in good condition, and if any faults are detected, inform the master.
2.4. Inspect the scaffolding and scaffoldings installed for work; in case of detection of any defects or deficiencies to inform the master.
2.5. When working indoors, make sure that the lighting is adequate;
2.6. Check the presence of external protective visors and fences of window and door openings, openings in the floorings and ceilings.
2.7. When working inside an operating workshop (if any work is being done on the workplace of a bricklayer or cranes are passing nearby), check whether there are necessary protective and protective devices. 3. REQUIREMENTS OF LABOR PROTECTION DURING WORK A. When laying foundations
3.1. When laying the foundations, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the state of attachment of the soil. If there are cracks in the slopes or faults in fasteners that create the threat of a collapse, you should not begin work, but you must report them to the master in order to take appropriate measures.
The soil in the absence of slopes should be securely fastened throughout the depth of the notch.
3.2. It is necessary to go down into the pit and out of it along the ladders or the staircase, and in the trenches - along the ladders. It is forbidden to use fastener strut for descending into a trench.
3.3. To lower the foundation blocks into the trenches by a crane should be smooth, without rocking, jerking and jerking. It is forbidden to stand under the lower unit.
3.4. Suspension of the unit with a crane to the place of installation of the foundation should be made from the outside of the building under construction. Taking the block, you can not stand at the foot of the slope.
3.5. Disassembly of the block can be done only after its alignment and final installation.
3.6. To lower a rubble stone into a trench or a trench, if this work is not mechanized, it should only be on inclined chutes, after making sure that there are no workers there.
It is forbidden to dump a rubble stone in a trench or pit not along the gutters, as this can lead to severe injuries to the people below. In addition, a stone in the fall can knock out thrust and cause a collapse of the soil.
3.7. The platforms adjacent to the curb of the excavation or trench should not be loaded with materials closer than 0.5 m from the edge.
3.8. Backfilling of the sinuses laid out with the foundation should be made on both sides at the same time, since the filling of freshly laid masonry on one side causes unilateral pressure of the soil on the masonry and may cause it to collapse. To fill up the sinuses between the outer wall of the basement and the slope of the pit should be only after obtaining the permission of the manufacturer or master.
B. When laying walls
3.9. Brick should be placed along the erected building on pallets in the area of the crane.
3.10. The laying of the walls of buildings should be done only from floors or with properly installed scaffolding or scaffolding, (internal or external).
3.11.When laying the walls of the building to a height from the working floor and the distance from the masonry level from the outside of the wall to the ground (floor) more than 1.3 m, it is necessary to use fencing devices, and if it is impossible to use them - a safety belt.
3.12. It is not allowed to lay the walls of the subsequent floor without installing supporting structures for interfloor overlapping, as well as platforms and marches in the stairwells.
3.13. The maximum height of the erection of free-standing walls (without laying the floors) must be defined in the design of the work.
3.14. Laying of external walls with a thickness of 0.775 m in the standing position on the wall is not allowed.
When the wall thickness is more than 0, 75 m, it is allowed to make masonry from the wall using a safety belt attached to a special safety device.
3.15. It is allowed to remove temporary fastenings of elements of the cornice, as well as the formwork of brick lintels after the mortar reaches the strength established by the project.
3.16. When moving and supplying bricks, small blocks and materials to the workplace with the use of lifting equipment, pallets, containers and load handling devices should be used to prevent the load from falling.
3.17. When laying industrial brick pipes it is not allowed to perform work on the top of the pipe during a thunderstorm, at a wind speed of more than 15 m per second.
3.18. Above the loading point of the lift at a height of 2.5-5 m, protective double flooring of boards not less than 40 mm thick should be installed.
3.19. The laying of the walls below and at the level of the ceiling, arranged from precast concrete slabs, should be made from the scaffolding of the underlying floor.
3.20. It is not allowed to install floor slabs without the side of the brick which was previously laid out of brick two rows above the level of the laid slabs.
3.21. The filling of voids in the floor slabs should be carried out prior to their submission to the floors.
3.22. The jointing of the exterior joints of the masonry should be done from the floor or scaffolding after laying each row. No workers are allowed on the wall during this operation.
3.23. When laying walls with a height of more than 7 m around the perimeter of a standing building, the danger zone should be allocated with a panel fence 1.2 m high in accordance with the requirements of GOST 23407-78.
3.24. The boundary of the danger zone is set for the entire period of construction of the object at the highest height.
3.25. The laying of walls up to 7 m is allowed with the marking of the danger zone around the building’s perimeter with signal fencing in accordance with GOST 23407-78 and safety signs in accordance with the requirements of GOST 12.4.026-76.
3.26. If it is impossible to isolate a hazardous area (cramped conditions), organizational and technical measures to ensure occupational safety should be developed in the project of work.
3.27. The entrances to the standing building (structure) must be protected:
- from above - horizontal or with rise to the wall of the building at 15-20 ° with a continuous canopy;
- on the sides - solid wooden shields.
The width of the shed must be at least the width of the entrance to the building and in any case - not less than 1.8 m, height not less than 2.2 m, length - from the wall of the building to the border of the danger zone. The end of the visor is equipped with an onboard board with a height of at least 0.15 m.
3.28. Above the entrances to the stairwells, when laying the walls with internal scaffolds, awnings of plan size 2 to 2 m should be arranged.
3.29. At industrial construction, masonry walls must be tested with tubular or other scaffolding installed outside or inside the building.
3.30. Fill the frame with brickwork, you can with suspended scaffolding.
3.31. In residential construction, masonry should be carried out from internal scaffoldings that are moved from one floor to another.
3.32. It is prohibited to arrange scaffolding on random supports (barrels, boxes, bricks, etc.).
3.33. With an insufficient width of the flooring and the absence of fences, as well as on scaffolding, the ends of the boards which are left on the weight, it is not allowed to work. Work flooring should be smooth and not sag from walking on it.
3.34. One of the basic conditions for the safety of a bricklayer is the rational organization of his workplace, which includes the following requirements:
- the use of properly arranged inventory scaffolding, tested before the work of the master;
- the correct location of the brick and mortar; c) cleanliness and order in the workplace.
3.35. The scaffolding on which materials are placed with brickwork must be at least 2.4 m wide. The flooring area in this case is divided into three zones: working (50-60 cm wide, adjacent to the wall being laid out), materials storage (80- width wide). 90 cm), transportation of materials and the passage of workers (1-1.1 m wide).
3.36. In the case of tape installation, the scaffolding must be arranged at the edge of the fencing floor (railing) with a height not lower than 1.1 m, consisting of (racks and three horizontal boards (railing middle and lower (side)) attached to the inner side of the racks.
The board must be at least 15 cm high. On tubular woods, railings and middle boards can be replaced with pipes.
3. 37. Scaffolding and scaffolding can not be overloaded with materials and litter.
In order to prevent overloading of working flooring, posters should be displayed in prominent places indicating the location, number and capacity of brick packages and crates with mortar. The load on the scaffolding and scaffolding shall not exceed 250 kg / m2.
3.38. When batch filing bricks and pallets captures must have fences.
3.39. The level of masonry after each movement of the mixing means must be not less than 0.7 m above the level of the working floor or overlap. If it is necessary to produce masonry below this level, the masonry should be carried out using safety belts or special mesh protective fences.
3.40. The gap left between the wall and the flooring to check the masonry should be no more than 5 cm. It is necessary to ensure that no objects fall through the gaps.
3.41. It is allowed to make masonry walls with wooden floors only if they have solid flooring laid on the floor beams. It is strictly forbidden to walk on the side of a wooden floor and install racks on the forward.
3.42. The masonry of the walls after the transition of masons to the ceiling, mounted from large-panel reinforced concrete slabs, should only be from a mark of at least 5 cm from the top of the ceiling. To do this, when bringing the brickwork of the wall to the level of the overlap, it should not be interrupted, but continue 15 cm above the top level of the floor slabs; at the same time, it is necessary to leave ledges for laying the overlapping panels so that when going over to the overlap, the mason has in front of him a so-called side.
3.43. Laying of the side at the level of overlap should be carried out with scaffolding installed on the lower floor.
3.44. It is forbidden to install floor slabs without a lined side.
3.45. Balcony plates are recommended to be supplied to the installation site with protective grills pre-installed on them.
3.46. When mounting, balcony plates must be supported by two special temporary stands mounted on the balcony slab of the underlying floor on a wooden lining.
3.47. Lifting slabs must be engaged with grippers for all four mounting loops. Before lifting the slab, it is necessary to check the reliability of the engagement of the gripping device. It is prohibited to mount plates that have damaged mounting loops or other defects.
3.48. It is forbidden to perform any work or be under the floor slab during its raising and lowering.
3.49. It is prohibited to feed the plates by turning the boom through the work of masons and installers. Floor slabs must be supplied from the outside of the building.
3.50. All workers of the integrated brigade must be aware of a single alarm system adopted during the installation of floor slabs.
Signals and commands to the crane operator should be given by one person - the signalman.
3.51. To ensure safety when working on the edge of the wall, it is necessary to install exhaust work platforms with barriers.
3.52. Laying of floor slabs must be started from the end walls. The first plates should be taken from portable tables, the subsequent ones should be laid from previously laid plates.
3.53. Workers, laying the floor slabs, must ensure that they are not swaying while lowering them on the wall.
3.54. In order to avoid the destruction of the side of the mounted plates should lower the plate at the level of 0.5-0.8 m from the support balance, and then smoothly, without swinging lower to the support.
3.55. The hemming and cutting of bricks and ceramic stones should be made in protective glasses. It is forbidden to chop ceramic stones on the wall.
3.54. On staircases, fencing should be placed on window openings, on platforms and on marches.
In the absence of interfloor ceilings in adjacent rooms, the openings of internal walls should also be fenced.
3.55. In case of violation of the accepted work procedure and detection of defects in scaffolding, scaffolding and protective visors, you must immediately inform the master or the manufacturer of the work and stop work until instructions are received on the possibility of its continuation.
3.56. Prefabricated lintels overlapping window and door openings should rest on the walls of at least 25 cm in length on each side.
3.57. When facing the facade with plates or blocks, which is done by laying, you should wear a safety belt and tie it to reliable parts of the building.
Breaks in masonry, performed simultaneously with the outer lining, are allowed only after laying the walls to the level of the upper edge of the facing plates or blocks.
3.58. Brick eaves, protruding beyond the wall of more than 30 cm, you need to put only with external exhaust, suspended or rack scaffolding, but not with the wall and not with internal scaffolding.
The flooring of the produced forests must be not less than 60 cm wider than the eaves.
3.60. When the device eaves, protruding less than 50 cm, laying can be done with internal scaffolding, with the bricks must be laid towards the outer plane of the wall so that the front row was the last.
3.61. In winter time it is necessary:
- the workplace is constantly cleaned of snow and ice:
- when laying walls by the method of freezing, use more durable solutions prepared with heated water;
- it is possible to arrange the eaves by means of freezing only if their carrying out is less than the wall thickness;
- with the onset of a thaw, monitor the condition of the masonry made by freezing, and in case of uneven precipitation, take measures against its collapse;
- when heating the brickwork with steam, be careful of burns;
- when working in hot houses, make sure that heating devices are tested with a test furnace before use.
3.62. When heated by a furnace, the smoke should be removed by separate pipes. It is prohibited to heat various types of braziers, as well as to use kerosene, gasoline, etc. for kindling.
3.63. When performing brickwork by the method of electrical heating, fences and posters with warning signs should be installed that prohibit unauthorized access to the heating areas.
Work with the use of electric heating requires special care.
The masonry section, which is under electric heating, must be under the direct supervision of an electrician on duty.
3.64. It is prohibited to perform any work on the electric heating section when the current is turned on. 4. REQUIREMENTS OF LABOR PROTECTION IN EMERGENCY SITUATIONS 4.1. In the event of a malfunction of the pallet with a brick at the time of moving it with a crane, the bricklayer must go out of the danger zone and give a “Stop” signal to the crane operator. After that, the brick should be lowered to the ground and transferred to a working pallet.
4.2. If cracks or displacement of the brickwork are detected, the work should be stopped immediately and notify the supervisor.
4.3. In the event of a landslide or violation of the integrity of the mounting slopes of the excavation, masons must stop laying the foundation, leave the workplace and report the incident to the work supervisor. 5. REQUIREMENTS OF LABOR PROTECTION AT THE END OF WORK 5.1. Mason must:
- remove the remaining bricks and tools from the wall, clearing it from the mortar;
- clean and put in order the workplace and aisles;
- when working at a height, descend down only along the ladders or capital main stairs; to use ladders or cargo lifts for the descent down is strictly prohibited:
- hand over overalls: dry - in the wardrobe, and wet - in the dryer;
- wash hands and face thoroughly. For this instruction on labor protection, thank Sergey 😉
|