Consider first the process of cutting with a chisel along with a hammer.
The chisels, in their cutting part, represent the shape of a wedge. The choice of sharpening angle largely depends on the hardness of the material being processed.
the harder the material, the dumber the wedge.
Recommendations for selection
steel angle of the cutting wedge is 60 degrees,
non-ferrous metals the angle of the cutting wedge is 35 -40 degrees.
To obtain grooves using a chisel, a special chisel is used.
When machining with a chop, a hammer weighing up to 500 g is used.
Cutting process
In the process of cutting the workpiece is fixed in a vice a little to the left of the right edge of the jaws. The remaining space is used to attach the chisel. The hammer is positioned briskly to the left and placed on the workbench to the right of the vice, while the chisel is to the left, the cutting part to itself. The workplace must be protected by a safety net to protect against flying fragments of material.
Features of body position
In the process of cutting metal, it is important to monitor the correctness of the working posture. It is necessary to stand straight when felling, the body should be turned so that the right shoulder is opposite the chisel head. To improve the stability of the body, the left foot should be pushed forward and the weight transferred to the right foot.
The chisel with a hammer is held in such a way that the edge of the handle and the impact part protrude by 20-30 mm.
Features of felling There are two ways to chop metal
1. Cutting in a vice for marking risks.
2. Felling in a vise clamping metal not at the level of the vise jaws
Cutting with the help of a vice with the help of marking marks is carried out in such a way that the marking is 1.5-2 mm above the jaws of the vice itself. The chisel is placed at an angle of 30-40 ° to the workpiece surface. After each stroke, the instrument must be returned to its original position.
The cutting in the vice clamping the metal at the level of the jaws of the vice is carried out if the risks are lowered below the level of the jaws, so that after cutting the surface of the part has an allowance of up to 1.5 mm.
With different hardness of the material there are different types of cuttings.
1. Wrist types of cuttings.
2. Elbow types of cuttings.
3. Shoulder types of felling.
Very small irregularities are removed by the wavy view of the cabin.
Elbow types of logging - remove unnecessary material and cut into pieces the workpiece with a thickness of no more than 10 mm.
Shoulder type of logging - remove a thick layer of metal and cut into pieces the billet large thickness.
Features of the felling
In the form of a wrist, it can be assumed that the hammer moves due to the movement of the hand.
When the elbow is seen, the arm bends at the elbow and the blow becomes stronger.
When the shoulder view moves from the shoulder and the blow becomes much stronger.
In case the logging harvest cannot be healed in a vice, it is processed on a plate. In this case, the chisel is placed vertically on the marking risk and it is only in this way that they are hit.
After each such impact, the chisel is moved to half of its cutting edge. This method makes it easy to install the chisel in the desired location, which contributes to a continuous cut. If the workpiece has a large thickness and simply does not cut it, then in this case additional marking risks are applied to the opposite side of the cabin. In this case, the workpiece is cut to about half the thickness on one side, then cut to the other side.
If you need to cut the workpiece on a complex profile, then the cutting edge is removed at a distance of 2 mm from the marking scratches, cutting the metal with light blows along the entire profile. Next, repeat the felling more powerful blows. Then turn it over and produce cutting along the contour indicated.
Features of safety when chopping metal
1. It is allowed to work only with a serviceable tool that does not have cracks and burrs on the impact part.
2. The handle of the hammer is firmly mounted on the lugs and not have cracks.
3. You can not check the quality of cutting by hand to touch.
4. At the end of the cutting, the impact force must be weakened.
5. Cutting metal should be made in protective glasses or behind a protective screen.
Mechanical chopping is performed
using pneumatic chipping hammers
using presses
using press scissors
using various modern methods of cutting (waterjet, laser cutting, air pressure cutting).
Felling with pneumatic chipping hammers
Pneumatic hammers are used for cutting metal, chasing seams, chipping edges for subsequent welding. Sometimes they are also used for stripping seams after welding, cutting complex grooves. In the workshops they are used to smooth the joints of water and sewer cast-iron pipes and punching holes and openings in the walls. In construction, chipping hammers IP-4108 and IP-4126 are used, the designs of which have few differences.
Pneumatic chipping hammers
It should be noted that the air hammer has a vibration-proof manipulator protecting the worker’s left hand from vibrations, increasing the accuracy of blade position control. The manipulator allows you to fasten the tool and thereby prevent the departure from the hammer when idle blows.
In Russia, the following types of pneumatic chipping hammers are produced:
hammer P-4126 is used for stripping seams and cutting out sinks.
iP-4108 hammer is used for stamping and stripping welds.
hammer MP-4 is used for easy cutting depth,
hammer MP-5 is used for the average depth of cutting,
the hammer MP-6 is used for deep cutting
Metal cutting with presses
Felling press has a number of features:
The press can chop metal of any thickness
The press can cut down the figures of any complexity, it depends on the stamp
The press is not profitable to use in small-scale and single production.
When working in the press you need to comply with labor protection measures, which are very extensive. The most important rule is that the worker does not in any way remove the protective cover of the press and not be in the working area. The second main rule is that before starting to cut, it is imperative to check the operation of the stamp at idle.
Cutting using press scissors
By itself, press scissors are very simple in design, so it is very easy to undergo an inexpensive repair.
This method can be cut metal with a thickness of 5 to 30 mm. In the process of cutting the worker needs to ensure that the knives do not go very deep into the workpiece. If the knives go in very deeply, then a double cut may be obtained. This is especially true when cutting scrap metal and workpieces with high ductility. Also when processing sometimes
Cutting with a press scissors is the most common type of cutting metal in production. In this method, the metal is separated very cleanly with almost no burrs and deformation of the surface layer. Modern press shears often equip CNC. This allows you to improve the quality of the cut and significantly reduce the complexity of cutting.
In the process of cutting the part, the metal is pulled out. The extruded metal is chopped by the press. The quality of press scissors is judged by the line of cutting metal: the smoother it is, the higher the quality of tooling.
The ratio of the cutting line to the fracture of the metal depends on the degree of wear of the shear press.
This method gives maximum cutting accuracy.
As with the case of the press press above, it is not beneficial to use scissors for small-scale and individual production.
Press scissors for the cabin of metal
1 disk;
2 hydraulic;
3 container.
All molds are divided depending on the possibility of moving to stationary and mobile.
Disk, sometimes referred to as lever, very well suited for small-scale cutting. Lever press scissors are attached with two knives, and one of the knives is attached to the frame. This makes most of the lever shear presses immobile. Knives for this tool are made from high carbon steel. The durability and accuracy of the cut depend on the quality of the knives, so I advise you to pay special attention when buying.
Hydraulic press shears have the same characteristics as the lever shears, but the main movement of them is driven by a hydraulic mechanism.
Container press scissors are a perfect container for cutting various scrap metal. This type of press scissors has a separate chamber where metal is thrown for cutting. Due to this feature, the chips do not fly apart during work, do not fly apart to the sides, which significantly increases the safety of the worker.
Container press shears vary in the way metal is fed
1 Automated
2 Manual
Container press shears vary in power - this greatly affects the maximum thickness of the metal being cut.
In this article, I talked about the main methods of cutting for metal intended for cutting in subsidiary farms and in industrial production. If you have questions, please write in the comments.
"Manufacture of wire products" - Products made flexible. Receptions manual bending wire. Bending sheet metal. Examples of wire products. Production of wire products. Practical work. Flexing blanks. Questions to fix. Tools and equipment for manual bending. Safety Instructions Bending in bending dies. "Cutting" - Milling. Pulling Honing. Deployment. Classification of machine tools by weight. Chiselling Classification of machine tools. Types of machining. Turning. Countersinking Kinds. Metal cutting machine. Grinding is called cutting metals with abrasive wheels. The machine tool has a drive. "Metal filing" - the formation of skills. Target rounds. Types of filing. Tools and fixtures. Learning by topic. Filing. Tool for control. Manual filing rules. File movement pattern. Filing flat surfaces. Familiarity with the tools. Final briefing. Inspection of appearance. "Projects on technology lessons" - Products from aluminum cans. Limiters for books. Clothespins. Bookshelves. Project themes for grade 6. Creative project at the lessons of technology. Pictures of wire. Selection and justification of the project. Project. Products with a list on a tree. Development options. Supports for CDs. The layout of the playground. "Metal Cutting" - Machine editing. Hack saw blade. Rules when working hacksaw. Bending Rihtovalny grandma. Gladilki. Kiyanok. The purpose of the cabin. Types of felling. Mechanization of cuttings. Toothed teeth. Edit bar. Cutting. Cutting is cutting. Chisel dimensions. The hacksaw is kept away from the face. Tooth canvases. Bending pipes. "Technology at school" - Needlework. Modeling, design and manufacture of clothing. Technology modules. Professional self-determination. Materials Science. Material technology. Sandwich fantasy. All that is in the furnace is swords on the table. Machine science. Cooking We must learn to understand work as creativity. Total 32 presentations
With thinning an ELHA unit can be used in apiaries 30–40 m wide. Sub-rifle-sights are laid at an angle to the technological corridor 60 0 and trees are cut into it with an electric saw. She also pruned boughs. Khlysty strel for the top.
Could get the application and promising options "Woodpeckers". In 1984, a sample of MVP-20 on a self-propelled chassis with a 6-meter reach of a manipulator, cutting down trees up to 22 cm, was exhibited at an exhibition in Moscow. The Woodpecker-1D variant, which has a trunk drive on an arrow, is highly productive.
Since “Woodpeckers” only lay trees on the dredge, for their skidding they used the skimmer of the “Ant” whip packs, which is aggregated with a T-40A, MTZ-52 tractor and other narrow machines with four driving wheels. The skimmer is an arrow lifting a pack of trees (whips) behind the comms.
The felling-buncher “Dyatel-2” (LP-2), created on the basis of a TDT-55 tractor with a second cab on a turntable and a boom length of 10.5 m, with a grip and a cantilever saw, was used on logging through logging when sampling large-sized trees. In its development, the machine was designed MVP-35 with one cabin and a storage on the boom. Eight trees with a trunk diameter of 8–14 cm can enter the drive. The LP-54 was prepared for release on the basis of a TT-4 tractor with a 10 m crane arm.
At thinning and open-cutting logging, the wide-cutting technology of logging works with technological corridors laid through 60-100 m is promoted. Trekking to them of trees, whips (half-whips), assortments is carried out with a winch LT-100, LT-400, LT-600, ML-2000M or tractor understudy PDT-1, PDT-0,3. For example, the LT-400 winch is mounted on a two-wheeled trolley, has a 65 m long cable and a base engine from a chainsaw, weighs 76 kg, is serviced by two people. Small whips trill bundles of up to 0.4 m 3 with the help of drags or chokers. Capacity with an average diameter of whips 10 cm - 12-14 m 3. Tractor trailer PDT-0,3besides a winch with a rope 65 m long, it has a hydraulic manipulator for transporting podtrelevannoy wood along portage.
Wide-range technology is especially recommended in forests with a dense network of roads, which are used as technological corridors. Ukraine has developed a thinning technology with a delimbing-bucking machine. Technological corridors 4 m wide lay across the rows of crops through 80 m. Trees are cutting with chainsaw for skidding for buttresses between row spans with a winch to the unit based on MTZ-82. Trees are processed with a maximum butt diameter of 35 cm. The assortments have a length of from 1.5 to 6.0 m (multiples of 1.5) and are rotated with another machine.
The most common technology of mechanized thinning and cutting logging is srednepishechnaya (31-50 m wide) with a shafts of a chainsaw and skidding trees or whips for the tops of agricultural wheeled tractors equipped with a winch and shield, or logging tool LTP-2, LTN-1. T-5L, T-40A, T-25, MTZ-52, TL-28 and other tractors have proven themselves well. In areas where there are no technological corridors, technological corridors are being prepared with a width of 2-3 m. More powerful tractors are also used: MTZ -82, MTZ-80 (with factory skidding winch), LKT-80 and crawler skidder TDT-55A, for which 4-5 m wide fiber is being prepared. UTG-4,8 hydraulic catch can be installed on MTZ-82 (80) .
The operating experience since 1982 of the forest wheel tractor LKT-80, produced by Czechoslovakia, confirmed the possibility of developing a stable running system in the forest. Preparing for serial production by CIS countries wheeled skidder LT-19equipped with a hydraulic manipulator to collect whips for the tops or for the combs using a tick grip. Its performance at a distance of 300 m - 30 m 3 per shift. It is planned to create a set of machines on the basis of a caterpillar tractor for work on overmoistened soils.
In the portage, trees begin to fall from the far end, retreating from the boundary of the cutting area to the height of the tree (there is no need for laying a portage here, which also prevents damage to the trees outside the cutting area), apex in the direction opposite to the skidding. In fallen trees, the branches are chopped off and placed near the growing trunks, so as not to damage the cambium trunks and roots during skidding. Then, from the nearest side of the apiary to the upper warehouse (loading area), trees are felled with a crown at the fiber at an angle to it no more than 40 0 for skidding logs at the top. The branches are chopped off and the nearest ones are carried to the portage to protect the soil and trees.
The branches, removed from the portage, are scattered or folded into small piles up to 0.5 m high. The exception is the winter logging in spruce-aspen stands, where, in order to avoid attracting elks, which damage spruce, logging should be carried out with the crown. In other cases, along with the whip skidding, wood skidding is possible with half-whips or assortments.
Burning of logging residues is mandatory in coniferous plantations on dry and fresh soils near the railways and near other fire-dangerous objects. In other cases, felling residues should be considered as a natural fertilizer. On dry and fresh poor soils (types of forest growing conditions A 0, A 1, A 2, B 1) scattering of forest residues in the Bryansk forest area increases the humidity of the upper soil horizons by 2 times, and the content of nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus in the litter 2-4 times. The soil temperature becomes optimal for the roots, which increases the growth of pine by 10-20% (Slyadev, 1971). To prevent the spread of fire, it is better to localize such areas with mineralized stripes. In Kazakhstan (in the field of dry forestry) crushing them with scattering along technological corridors at a distance of 10-20 m was effective for speeding up the mineralization of the branches and alleviating the fire danger. The LO-63B self-propelled ruber was mentioned for grinding.
It should be noted that agricultural tractors were not designed for work in the forest, and often have to repair the chassis. Because of this, foresters are forced to use skidders tracked tractors designed for clear cutting. But they require broad portages, causing great damage to the forest. Long overdue is the need for serial production of wheeled tractors with an active semi-trailer: TL-28 (6 kN) based on self-propelled chassis, ALP-1 (9 kN) based on T-40AM, etc. On the basis of MTZ-80, an assortment truck MTN-36 with a semi-trailer was developed PL-4 AOOT (Velikoluksky Plant) and PPD-6 semi-trailer loader (VNIILM).
When narrow apiaries for trouting logs and assortments used 10 meter skidder MTT-10 on the basis of MTZ-82 and LHT-55. In the case of assortment harvesting, the removal of assortments from the corridor lanes is carried out by an assortment truck, equipped with a manipulator for loading and unloading assortments up to 4.5 m long. The assortment truck carries wood to the logging road.
Log hoppers (forwarders) widely used in Scandinavia, where they work in combination with feller-delimbing-bucking machines (harvesters). The high productivity of workpieces (up to 6.0 m 3 / person-parts) in coniferous stands 20 m in height with a distance of 100 meters showed a feller-delimbing bucking machine Harvester Lokomo 919 / 750N with the removal stacked in the technological corridor 4 -meter timber log yard - forvader Lokomo with a 10-meter hydraulic manipulator. Within a radius of 5 m, the power saw of the harvester is fed to the trunk with a diameter of 6-50 cm. The length of the sawn timber is measured with an accuracy of ± 5 cm using a special roller, and information about the assortment is transmitted to the operator's cabin on the display. The branches are cut at the same time as the measuring and dismounting of the trunk and fall down in front of the car, weakening the formation of a track during further movement and the forwarder. To reduce root damage, the first track of the harvester is used for the forwarder. Then the first one, going deeper by 10 m, moves between the trees, placing assortments near the first ones, and, moving forward another 10 m, puts them near the future of its own track and passage of the log truck. So that the distance between the passes of the log truck is 25-30 m. Performance - 90-160 m 3.
Since 1989, they began to produce in our country, together with the company Terratek, of components from Finland, Sweden and other countries, domestic “harvesters” and “forwarders”. The tests of these machines and other Finnish-Swedish samples have not yet yielded satisfactory results, since about 20% of the cutting area with wet soil turns into deep (up to 20-80 cm) gauges with the root system of the nearby trees cut here, other external and internal trunks get damage (up to 30% of trees). This technique is acceptable in the winter or for even-gradual and clear cutting with preservation of undergrowth.
Finnish machine “Makery” turned out to be acceptable for thinning. This is a basic small-sized tractor, with a caterpillar chain on wheels, equipped in two versions, as a feller-buncher and feller-delimbing-bucking machine. Felling cutting knives cut trunks up to 25 cm in diameter. Machine width - 1620 mm, length - 2.6 m, height - 2.2 m, weight - 2-4 tons, engine power - 22 kW, traction force - 0.5 kN, capacity - 3.5-4.6 m 3 / h. It damages 5-10% of the number of trees and 10-15% of the soil surface (Nerman et al., 1984; Gilts et al., 1986).
Other new machines can be found on the “Index of current regulatory and technical documentation on standardization in forestry”.
For the organization and conduct of mechanized thinning, planning the need for technology, as well as labor and cash costs, drawing up projects for organizing forestry for certain regions of the country, settlement and technological cards (RTC) have been developed. The form of the production flow chart is given in the Manual for thinning.
BASES OF METAL HANDLING
Basic concepts of home theory, editing and markup
1.1.1 Theory of the basing of blanks. Base - surface, line, point, defining the position of the part in the node during processing or control. Distinguish the base design, technological and measuring.
Design bases - assigned during the design and determine the connecting dimensions in the node.
Technological bases - determine the position of the part (workpiece) in the machine relative to the heads, spindles, cutting tools. From them measure the dimensions in the manufacture of parts.
Measuring bases - determine the position of the surfaces of the parts relative to the measuring tool.
It is desirable that the design and technological bases coincide. For workpieces, the most treated surface is taken for technological bases; for cylindrical workpieces or workpieces with holes, a flat surface parallel to the axis of the surface or the axis of the holes; untreated blanks - one of the outer surfaces.
1.1.2 Editing - an operation designed to eliminate distortion of the shape of the blanks (dents, buckling, waviness, warping, curvature, etc.).
Editing is carried out on both cold and hot metal. Editing is carried out manually (on a steel or cast-iron plate or on the anvil); on the correct presses or in the correct rollers. For manual editing, use hammers made of soft materials (copper, lead, hard wood) with a round polished brisk or trowel and support (bars). For hardened blanks used hammers with a hardened shaped head.
The curvature of the blanks is checked by eye, by the gap between the alignment plate and the blank laid on it. Curved places are marked with chalk.
Raw material editing:
a) straightening a strip bent on a plane - on the most prominent places they are hit hard with a hammer or sledge hammer. As straightening the impact force is reduced, the workpiece is periodically turned over;
b) straightening steel strip curved on the edge - the workpiece is placed on the plate, dividing along the length into curvature zones approximately equal in width to the width. The blows are applied in rows from the center to the edges, starting from the most concave part, the force of the blows decreases from the most curved part to the less curved part (see rice 1.2, and);
c) editing twisted strips - carried out by the method of unwinding; one end of the workpiece is clamped in the metalwork (stationary) vice, the other - in the manual, unwinding is carried out by a lever inserted into the special. manual vise hole;
d) straightening sheet material - sweep and wavy places around with chalk; then hit the pattern (see rice 1.2, b), from edge to center the force of the blows
decreases; during editing, the sheet is turned over in a horizontal plane so that the blows are distributed in a circle over the entire area. If the sheet has a waviness, then it is ruled first; the sheet in the middle is drawn out and the undulation disappears.
a - steel strip; b - sheet material; in - the tempered square
Figure 1.2 Material Editing Schemes
d) editing thin sheets - is carried out with a wooden hammer (with a mallet) or with a textolite pad, which is placed on convex places; they are hit on defects with a hammer; foil materials are laid on a flat surface and ironed with a smoothing pad - even plates with rounded edges;
e) straightened hardened material - it is carried out by the metalwork or leveling hammer with the extended or rounded striker. The strip is placed with a bulge down, the blows are frequent, but not strong. Complex details rule the contour of the distortion, for example, corners. The scheme of strikes, their strength and direction are shown in fig.1.3, c.
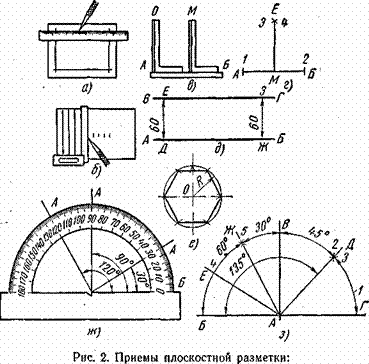
1.1.3 Layout. Preparation of materials for work. To markup the surface is prepared in the following sequence.
1 Preparation of dyes. For coloring untreated surfaces (castings, forgings, rolled products), a chalk solution is used (ground chalk is diluted in water). To protect the paint layer from abrasion and for its quick drying, wood glue is introduced into the dye composition (600 g of chalk and 50 g of wood glue per 4 liters of water).
Purely processed surfaces of the products are painted with a solution of copper sulfate (two to three teaspoons of copper sulfate crystals in a glass of water) or a special marking varnish.
2 Preparation of the blank for painting. When preparing blanks for painting, they are cleaned of dust, dirt, scale and rust with a steel brush. Plates should not have burrs and sharp corners. One plate is sanded from both sides with a sandpaper, and the planes of the other plates are left untreated.
3 Painting surfaces. When applying the dye, the blank is held in its left hand in an inclined position.

Figure 1.3 techniques for painting surfaces before marking.
A thin and uniform layer of the dye is applied to the plane by vertical and horizontal cross-brush movements. The solution should be recruited only with the end of the brush in a small amount to avoid the formation of smudges. Peeled planes are stained with vitriol solution, and untreated planes are painted with chalk solution. After the end of the staining plate must be dried.
4 Markup- drawing on the surface of the marking lines (scratches), which show the processing limits of the workpiece. Distinguish between flat and spatial markup. (The difference is on its own).

a - scriber; b - double reismas; in - shtangenreysmas; d - center punch;
d - marking line before processing; e - marking line after processing
Figure 1.4 Tools for marking work
When marking use three types of tools (see figure 1.4, a - g):
a) for applying and threading scratches - scriber, single or underdog reamers, ratchet-raisers, marking compasses, center pins;
b) for finding the centers of circles (holes) - center punch, center-finder, square-center detector, etc .;
c) devices for marking - gaskets, jacks, turning devices, vertical stands, dividing heads, center heads, etc.
Markup it is made on special marking plates from gray cast iron. The upper working plane and side surfaces of the slab must be scraped, dry and clean. At the end of the work, the stove is rubbed with dry rags, greased and covered with a wooden lid; metal dust and chips are cleaned with a scoop. There should be a special litter box nearby.
The workpiece must not be moved around the plate to avoid scratches and nicks. The plate is placed on a stable foundation in a lighted place. Provides general vertical and local lighting of the workplace.
Before work, the workpiece is cleaned with a steel brush and sandpaper for corrosion, scale and so on. Before marking it is necessary to study the detail drawing, compare the dimensions of the workpiece with the actual dimensions of the part, determine the technological bases. Then determine the type and sequence of operations markup.
Receptions plane markings. First, all horizontal lines and risks are plotted, then all vertical ones, then oblique ones. Circles, arcs and mates are applied last. If center risks are selected as the technological base, then the markup begins with them. The markup is finished if the image on the plane fully corresponds to the drawing of the part.
Straight lines are applied with a scoop tilted away from the ruler. The ruler or square is tightly pressed to the workpiece, hold the line once, without interrupting the movement of the hand. If the line (risk) did not work, it is painted over and carried out again. The division of the circle into equal parts is made by geometric constructions or using special tables. For the marking of a batch of identical parts using templates that are made from sheet steel. The configuration and size of the template must exactly match the drawing details.
Spatial markup techniques. The difficulty of spatial marking is the need to link the markings of various surfaces with each other.
As a technological base, a surface is selected, relative to which it is possible to mark the greatest number of axes or planes, set
the main axis of the workpiece, the number of its positions on the plate and the sequence of marking.
The workpiece is firmly installed, without swinging, on the marking plate so that each axis or plane of the part is perpendicular to the common plane of the plate. For installation and alignment of the workpiece using prisms, support pads, jacks, marking cubes and special tools (for example, swivel). The first installation is made so that it is convenient to start the layout from the selected technological base.
Spatial markup techniques are basically the same as planar marking techniques.
Coreing marking markings. After marking the lines are nicked. The punch is taken with three fingers of the left hand (thumb, index and middle). The tip of the center punch is placed exactly in the middle of the risks or at the point of intersection of the risks. Before the impact, the center pins are slightly deflected away from themselves, and at the moment of impact they are turned vertically. The intended and hooked part is shown in fig.1.4, d, e.
Practical lesson on “Drawing up a route map for marking the material”. Time - 2 hours.
10 Lecture 2
Cutting and cutting of metal
1.2.1 Cutting blanks is carried out using a special cutting tool: chisels ( figure 1.5, but) kreutzmeysel ( figure 1.5 b) or gutter ( figure 1.5, in). Cutting is performed in cases when high precision of machining is not required or when the part cannot be machined. With the help of cutting, remove the extra metal layer from the workpiece, cut the workpiece into parts, cut holes, cut through lubrication grooves, etc. Cutting of small blanks produced in a vice; large pieces are chopped up on a slab or on an anvil.
The chisel consists of three parts: working - 2
, medium - 3
and shock - 4
(peen) Wedge cutting edge - 1
and the hammer is tempered and released (edge HRC - 56 ... 61, hammer - HRC 37 ... 41). The values of the cutting edge taper angle are given in table 1.1. The kreytsmeysel differs from a chisel in a narrower cutting edge. It is used for cutting out narrow grooves. The grooves have a curved shape of the cutting edge and the working part.
The quality and productivity of logging depend on the force of impact with a hammer and the position of the chisel. With a brush stroke, only the hand with a hammer is bent. Such a blow is used to perform accurate and easy work. With an elbow stroke, the arm bends at the elbow, and the blow is stronger. The frequency of blows: with a hand stroke - 40-60 beats per minute, with an elbow blow - 30-40 beats per minute. The angle between the workpiece (the upper plane of the jaws jaws) and the axis of the chisel should be 45 o, the angle of inclination of the chisel should be 30-35 o.
Table 1.1 - the angles of the taper of the cutting part
When chopping a strip and sheet metal part of the workpiece, leaving the chips. It should be located above the jaws of the vice, and the risk of marking - exactly at the level of the jaws without distortions. When chopping metal on a wide flat surface, marking risks should protrude 5–10 mm above the jaws. At the same time, the grooves with a width of 8-10 mm are cut through with a chopstick first. The gaps between the grooves should be 0.8 times the length of the cutting edge of the chisel. Then the chisel hew down the formed protrusions.
When cutting fragile materials, they do not reach the opposite edge of the workpiece 1.5–2 mm or are preliminarily beveled at an angle of 45 o. Then, the remaining irregularities clean the groove, they also give the groove the final depth, width and shape.
When cutting out a shaped piece of sheet material, the latter is placed on a plate or an anvil. Initially, with wrist strokes, the intended contour is cut to a depth of 2-3 mm. Next sheet cut with strong elbow strokes. If the sheet is thick, it is turned over and finally cut through on the reverse side.
Manual chopping is a heavy and inefficient operation. To facilitate the work of the locksmith used air hammers (knife switches or riveters). The domestic industry produces pneumatic klepalniki brands KE-16 - KE-32 weighing 8-12 kg and lightweight riveters MP-4 - MP-5 weighing 4.2 kg.

a - chisel; b - kretsmeysel; c - trenchman
Figure 1.5 Tool for cutting metal
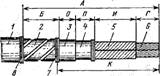
1.2.2 Cutting - separation of the workpiece into parts by hand or mechanized method. Manual cutting, depending on the profile of the workpiece and the cross-sectional area, is produced with jigsaws, metal shears, and gas-flame burners.
The most common cutting hacksaw. Hacksaw (see figure 1.6, and) consists of a frame (machine) 2
in which the steel plate with teeth is clamped (hacksaw blade) 5
. The saw blade is inserted into the fixed slot 3
and rolling 6
prismatic heads and pinned. The blade is tensioned with a wing nut. 1
. To reduce friction on the side surfaces of the teeth of the hacksaw blade is bred in different directions. The layout of the teeth do the tooth or on the canvas. Depending on the material. From which the web is made, cutting is done with a certain frequency: tool alloyed steels - no more than 60 double passes per minute, tool carbon steels - no more than 30.
When cutting, the workpiece is firmly clamped in the metal vice, ensuring the minimum distance between the line of jaws and the line of cut. When cutting thin steel blanks or blanks from a soft material, it is clamped between two wooden bars and sawing is performed together with them. When cutting thick-walled blanks, the cut is not completed by 3-5 mm. After cutting the workpiece breaks off.
When cutting blanks from materials with low thermal conductivity (plastics), the cutting zone must be watered with water or kerosene.
Sheet material is cut with scissors for metal. To mechanize the process of cutting sheet material, electric or pneumatic shears are used.
The working part of the electric scissors is shown in figure 1.6, b. Slider 4
placed inside the enclosure 3
gearbox and together with a movable knife 6
makes reciprocating motion. Fixed knife 2
mounted on a snail-shaped holder 7
. adjustment of knives is carried out by an eccentric 5
and a nut 1
.

and - a manual hacksaw; b - electric scissors;
Figure 1.6 Metal cutting tool
1.2.3 Procedure for compiling route maps.To perform plumbing and other work with the material, a route map is compiled - a list of operations for the sequential execution of work. The route map is usually a technologist for the worker. It includes the following sections (columns of the table):
- operation number;
- the name of the operation;
- a graphic image (what changes occur with the workpiece) with dimensional characteristics;
- equipment of the operation, i.e., a list of tools (devices, equipment, materials);
- a brief description of the actions;
- notes, auxiliary information.
An example of such a card can be seen in table 1.2.
Table 1.2 - Route map of the technological operation (sample)
| Operation Number | the name of the operation | Graphic image | Operation equipment | Brief description of actions | Note |
| I - the layout of the workpiece |
|
|
| Drawing axes of symmetry |
|
|
|
|
|
| Mark the center of the hole |
|
|
|
|
| …
|
|
|
|
|
|
| II –Selection of holes and grooves |
|
|
| Drilling center hole Æ20 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Selection of 2 holes 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Sample open slot (40x15) mm |
|
|
|
|
| III - Contour processing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Metal processing is enclosed in several operations, one of which is cutting. In this case, the workpiece is divided into more convenient pieces, anticipating the cutting process. Further details of the ways in which metal cutting is performed, possible problems, the difference between mechanical and manual operation and the types of equipment used. The cutting of metal is a metalwork operation, concluded in the impact of a cutting or impact tool on a metal workpiece. The process allows you to divide it into parts, get rid of extra layers of material, as well as get grooves and grooves. A cutting tool or chisel serves as a cutting tool for metal cutting, and a hammer is a shock. The latter is always used for manual work, and the first two are used depending on the desired result. The chisel is designed for rough work and deburring. It consists of 3 parts: - working (cutting);
- medium (the master holds a chisel for it);
- shock (beat it with a hammer).
Creutzmeisel is a tool for cutting out grooves and narrow grooves; for wide, a modified fixture with a different cutting edge shape (“trench”) is used.
Manual processing of workpieces in production is an energy-intensive and inefficient process. Often it is replaced by mechanical. The sequence of cutting the metal with a chisel is as follows: - the workpiece is placed on a slab or anvil, and better - mounted in a vice;
- the chisel is placed on the marking line (the place of cutting) vertically;
- hammer lightly strikes the contour;
- followed by deep cutting along the developed contour;
- billet flips;
- chisel strokes are made on the other side before the end of the felling.
It is important to leave a small part of the blade in the cut-out groove for the process to be accurate. Now - a couple of words about the problems arising during the manual cutting of the metal. Possible defectsManual cutting of metal is bad because there is a possibility of damage to the workpiece, although the whole process was strictly controlled. The following are common defects and their causes. - Curvilinearity of the cut off edge (weak fixing of the part in a vice).
- The edge is “torn” (the blows were made with a blunt chisel or an incorrectly sharpened crossbridge).
- Parallelism of the sides of the product is violated (skewing of risks or blanks in a vice).
- The depth of the grooves varies in length (the slope of the kreuzmeisel was not adjusted; the blow was uneven).
- The appearance of notches on the details (dull chisel).
- The presence of chips on the edge of the part or inside the groove (the chamfer was not removed from the workpiece).
To avoid these problems and not to spoil the metal pattern for work, it is recommended to follow a number of rules: - firmly fasten the part, if possible;
- keep the chisel angle at least 30 degrees;
- accurately mark the workpiece;
- work only with sharpened chisel and crossbridge, follow the angle of inclination;
- remove chamfers from parts before work;
- strike evenly.
Manual cutting of sheet metal was the only way to work 50 years ago. Today, the services of masters - equipment that requires them to only timely control, working accurately, efficiently and without damage to the workpieces. Guillotine cutting machinesAny enterprise occupying with release or production of metal rolling is equipped with the special equipment. The advantages of its implementation are obvious: - labor productivity is growing;
- personnel safety is ensured;
- material processing becomes better.
The most famous machine for cutting metal in the production environment is known as the "guillotine". It happens: - manual;
- mechanical;
- hydraulic.
The first is a compact device for local work. Cuts sheet metal of small thickness (up to 0.5 mm) and is driven by human effort. The use of a manual machine for cutting reinforcement, iron, steel and other products is more efficient than working with a chisel or chassis bar, but labor productivity will still be low. The reason is the need for human effort. Equipped with a foot drive. Its dimensions are impressive, and the allowable thickness of materials for cutting is increased to 0.7 mm. By using the strength of the legs, not the arms, productivity increases by a few percent. The stand-alone hydraulic guillotine, which operates autonomously and does not require human intervention. Equipped with a control unit, which sets up to a dozen parameters (type of metal, angle of cut, and others). The allowable thickness of the workpiece varies depending on the model and reaches several millimeters. The listed types of metal cuttings are complemented by equipment that is structurally different from the guillotines and has an expanded scope of application. Features of the combined devicesThe equipment includes press scissors and angle-cutting machines. The first chop and cut strip, sheet, shaped, long products. Press scissors are indispensable when punching holes in blanks, cutting open open slots. These combined cutting machines cope with any profile (channel, angle, brands / I, circle, square and others). Uglovysechnye machines are also called cutting stamps. They are distinguished by: - simplicity of design;
- high performance;
- increased output accuracy.
Used for angular processing of any materials. The compact design includes a measuring scale and chisels that provide chopping. The stamp for the process is selected depending on the thickness of the sheets. Some tools used in the cutting of metal combine manual and mechanized labor. These include: - pneumatic and electric chipping hammers;
- special machines, where standard chisel cutting techniques are accelerated 5-10 times thanks to the use of special tools.
So that you have a clear idea of the characteristics of the devices, we next consider one example. In particular, the machine for cutting rebar CSF 172. Device FeaturesThe machine tool CSF 172 is designed for cutting rebar, strips, metal profiles with a maximum allowable tensile strength of 470 MPa. It has several modifications: - SMZH-172 A (continuous knife travel);
- SMZH-172 BAM (continuous and single move).
The chipping machine for the CSF 172 fittings has the following technical characteristics: - power - 3 kW;
- diameter of rebar to be cut - up to 40 mm;
- strip dimensions - 40x12 mm;
- cutting a square with a side of up to 36 mm;
- backstage speed - 33 rpm (9 rpm - for a single move);
- maximum force - 350 kN;
- weight - 430/450 kg.
The design of the machine for cutting armature cmzh 172 supplemented by an adjustable stop with rack gearing, which allows you to get a smooth perpendicular cut. The advantages of using equipment are: - the possibility of replacing consumable items (blades) in the workplace without the help of special stands;
- long-term storage of the machine is acceptable if it is not used (in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations);
- ease of disassembling the mechanism in order to adjust the parameters.
The machine is unique, because it can work autonomously (continuous movement of the chisel), and at the right time (single stroke when pressing the handle). Guillotine felling, for example, does not yet possess such functionality. You can see the operation of the CSF 172 machine on the video below. Video: Manual cutting of metal on a CSF 172 machine. Cutting metal blanks - one of the main production processes. In place of heavy human labor comes machine, and this is worth using. The listed tools for cutting materials cope with different blanks. It is only important to choose the right equipment.
|