Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Expansion joints in buildings
- Chaber - what is it and its purpose
- Sharpening wood cutters: manual work, using grinding wheels and a grinding machine
- Belts and sandriks, crackers and volutes - secret codes of architecture on the example of the old Saratov Sandriks in architecture
- Surface grit - tooling work
- Maximum load on the balcony slab: how much can a balcony withstand in a panel house?
- Projects: symbols on drawings for water supply and sewage
- Marking and marking details How to mark the details with curved contours
- Tools for slotting Tools for slotting
- Tools for chiseling Slotting tools
Advertising
| Constructions of spiked joints in woodworking. The main types of connections of wooden parts. Conductor use for bracing |
|
Another master class, I must say that it is quite detailed and not less useful from Alexander. Today we talk about spike connection. Straight thorn is the foundation of joinery. How to perform it in artisanal conditions (and at the same time in an equipped carpentry workshop) and will tell our today's lesson. Consider the basic principles of manufacturing compounds on the spike on the example of two blanks on the wide and narrow, the thickness of all parts will be 30 mm. To begin, we mark the width of the blanks. Then it is necessary to postpone the hangers, usually it is 1/3 of the material - retreat 1 cm inwards, make a note With the help of a boring machine - his already considered. (By the way, you can use a conventional drilling machine). First, drill several adjacent holes. Then moving the workpiece from side to side with a recessed drill bit, cut off the remaining jumpers. This is the groove - with the help of a professional drilling-grooving device, after which you do not need to bend the spikes First, we make a cut on the marking line, then shifting the workpiece gradually remove the excess material. We turn over preparation and we repeat manipulations from all directions. The result is such a spiked thorn. But it needs a little refinement. in the same way we bypass a thorn from all directions. Everything turns out in one pass - much faster than the carriage. We segment the spike with the same circular. We remove the gap, adjusting the disc departure. Well, the spike with the groove is made, we turn to their connection. It should be adhesive. When sticking it is necessary to lubricate the groove from the inside or the eye, as it is necessary to coat the surface of the spike.
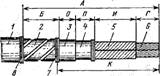
With the help of spikes, parts are joined in length, width and angle. Connecting the ends of parts in a half-tree. Such compounds may be length, terminal and median. For the manufacture of wood cut down in places of pairing on the thickness of the mating part. The length of the elements of the connection in length is 2-2.5 thickness of the parts to be joined. The elements of the connections are fixed together by gluing. Corner end connections (CC). The greatest simplicity and high strength are characterized by connections to open straight through thorns. A significant disadvantage of these compounds is that the ends of their elements are visible on both sides of the part, which degrades the appearance. Therefore, such compounds are used in those structures where it is possible to close the spikes overhead or in contact with them details. Connection to open through single spike (UK-1); the thickness of the spike (S1) and shoulder (S2) in this compound is calculated according to the following formulas (a): S1 = 0.4 S0; S2 = 0.5 (S0 - S1), where S0 is the part thickness. More durable compounds of this group are the compounds on the open through double CC-2 (fig. B) and triple CC-3 spikes (fig. C). To make such joints, exact dimensions and cutting of the joining elements are necessary. Spike Couplings with Polupotemkom , (fig. d, e) have a more complex shape, and therefore they are more difficult to manufacture. The thickness of the spikes of these compounds is calculated similarly to the thickness of the compound UK-1. These connections can be made with a non-through stud CC-4 (fig. D) and a through stud MC-5 (fig. D). The strength of the connection of the UK-4 and UK-5 inferior to the above compounds. They are used in cases when high joint strength is not required and it is necessary to avoid damage to the appearance of the part associated with the butt of the other part. Thorn connections (Fig. g, e) can be with a through UK-7 and a blind UK-6 thorn. The thickness of the spike and the shoulders is determined in the same way as in the joints with the semiflow open through single spike. Connections for round studs (dowels) somewhat inferior in strength to straight open spikes. However, give some wood savings. Previously, dowels were made mainly from solid hardwood, but now widely used dowels made of plastic. These compounds are also characterized by ease of manufacture. To do this, you need to drill the holes of the required diameter, install spikes on the glue and hold the parts in the mating under pressure. The diameter of the pin in the connection to the round plug-in spikes is calculated according to the following formula: d = 0.4S0. In the connection of UK-9, the use of through thorns is allowed (Fig. 1). Connections on the "mustache" with a plug flat spike may have through (UK-11) and non-through (UK-10) spikes (Fig. K, l). These compounds are characterized by low strength and more complex manufacture compared to the connections on round plug-in spikes. They have a beautiful appearance and provide a uniform color when finishing (especially non-through). The thickness of the spike of compounds UK-10 and UK-11 is determined by the formula S1 = 0.4S0. The connection is allowed on the “mustache” with a double plug-in spike, with S1 = 0.2S0. Gear connection UK-12 - This is a new kind of connection, the elements of which are performed on the machines. Thorns and their species. Spike called the protrusion on the part, whose width is less than the width of the part itself. Thorns are inserted into the slots. The nest should be of such size that the spike fits tightly into it. At the same time, the spike cannot be too thick, since it could crack a part when it is inserted into the socket. The spike has a length, thickness and width. Tire length - is the distance from the end to the shoulders, thickness - the distance between the shoulders or cheeks, and width - the transverse size of the cheek. Spikes are integral and inserted. Integral spikes are made at the ends of the parts to be joined. Solid spikes are usually flat. . Plugin spikes can be flat and round. For the strength of the joints, the one-piece and plug-in spikes are the same. Spikes can be through and deaf . Through the spike, when connected with the eye or through nest, passes through the mating part through. Deaf spikes mate with blind nests, the depth of which is not less than 2 mm long than the length of the spike. The number, shape and size of the spikes significantly affect the strength of the connection. The shape of the spikes can be round, flat and trapezoid. The edges of the trapezoid and flat spines are called cheeks. Shoulders - This is the cut part of the bar, that is, the surface above which the spike rises. The end of the spike is called butt . Screws and their types. Screw (screw from the German schraube) is the advanced screw itself, which is screwed into the soft material (wood) and forms the thread itself by deforming the material, that is, it is one of the 6 simplest mechanisms and changes direction or value depending on the applied force. Kinds: universal screws - this view is successfully used for a variety of surfaces. Universal used mainly in domestic work - construction and repair. Frequent thread with countersunk head, which has a slotted cross-thread - the distinctive features of such screws. Universal screws are made with different types of heads: countersunk, semicircular, cylindrical, hexagonal, with a cross-shaped slot. Further - hexagonal screws . They are made of cold-rolled steel and are available with dowels. Very durable, used in plumbing and working with wood. Frame screws are threaded all over the rod; used in the manufacture of various window frames and doorways. Here the dowel is not required. Screw ring welded provided with a steel ring instead of a head. It is applied not only in work with a tree, but also concrete, a brick. Allot round heads of screws, oval heads of screws and flat heads of screws. Round heads Screws are seen on the surface of the material in a screwed-up state and they are most likely to be twisted. Oval heads Screws are screwed flush, but still the head is a little stuck out. Flat heads The screws are mostly invisible and are called secret, because when screwed in, they become level with the surface. |
TREATMENT OF WOOD ON THREADED MACHINES Characteristics of spiked wood compounds and their requirements Connections on the thorns are widely used in the assembly of joinery, as well as when splicing short bars to obtain long materials. Products, individual elements of which are connected with the help of thorns, can be made in the form of frames and boxes. Frameworks include window frames, boxes, doors, vents, and various furniture items. The frame structure can be assembled from two longitudinal and two transverse bars without intermediate connecting elements or with middle bars in the form of bindings or grids. Spike connections are mainly performed on glue, sometimes to increase their strength, they are additionally reinforced with metal fasteners. At the location in the product spike connections are angular, middle and end. Corner spike connections are performed using flat rectangular (frame) or wedge (toothed) spikes (Fig. 130). A frame spike joint can be through a single (Fig. 130a) double (Fig. 130 6) or triple (Fig. 130 c) spike and a corresponding eyelet. Typically, the spikes are cut on the short (transverse) bars of the frame, and the lugs - on the long (longitudinal). The flat single frame spike (Fig. 130, a) consists of the following elements: two lateral faces (layers) 5, two shoulders 6, and an end face 4. The eye has two lateral formations 2, an inner end face 1 and two outer end faces 3 . Fig. 130. Angular spike end connections: a, b, in-frame on single, double and triple spikes; r-wedge spikes; d, e, g- “dovetail” with flat rounded and closed spikes; 1-bottom eye; 2,5-plate; 3-outer end faces; 4-end thorn; 6 spikes In addition to open end-to-end connections, there are non-through spike connections - on a spike with semi-darkening or darkening. In this case, the end face (top) of the spike is hidden or partially protrudes on the lateral external surface of the frame. In carpentry practice, spike joints are also used with the use of plug-in round studs (dowels) or flat studs. The ends of the connected bars in this case, protrude at an angle of 45 °. The wedge spikes for the corner end joint (Fig. 130 g) are formed with the same pitch for both bars at the ends that were previously buttered at an angle of 45 °. So that the sharp ends of the spikes do not protrude on the outer ears of the frame, before assembling at the ends of the blanks, they make a bevel 7 at an angle of 45 ° in size equal to the height of the spike. Corner joints with wedge studs provide sufficient strength and reliability. The corner end connection of wide boards when collecting boxes or boxes is carried out using rectangular spikes (Fig. 130 b, c) and dovetail spikes with flat (Fig. 130 d) or rounded (Fig. 130 e) edges. In furniture drawers, dovetail spikes are made closed on the front side (Fig. 130 g). In this case, the front wall should be thicker side.
Fig. 131. Median spike connections: a-flat single spike; b-straight rounded spike; in-median dovetail Angular middle spike joints are used when pairing the end of one bar with the middle part of another (Fig. 131). Such connections are in the form of a flat single spike and a rectangular blind or through nest (Fig. 131a). For large cross sections, parts are assembled on a double spike and two sockets. The connection with a straight or oblique rounded spike and an oval shape corresponding to it is shown in fig. 131 b, c. Cylindrical spikes (shkanty) and round holes, made by drilling, are also used as a connecting element. Sometimes, when assembling large-sized products, the dovetail median non-through connection is used. (Fig. 131 c). The shape and size of spiked elements determine the strength of the connection, so they are chosen depending on the design of the product. Spike connections along the length (splicing) are performed with the help of wedge (toothed) spikes. Wedge spikes can be with butt edges or pointed. The edges of the spikes are made flat or shaped, depending on the cutting tool used. The most widely distributed wedge spikes shown in Fig. 132. The main parameters of the connection - the length of the spike L and the pitch of the connection t. The spikes are blunted so that a gap S remains in the joints after pressing in.
Fig. 132. Wedge spike: L-length spike; t-step connection; S-gap The length distinguish between long (30-50 mm), medium (10 -20 mm) and small (3-5 mm) spikes. Standard spike dimensions are shown in Table 17. Depending on the location of the spikes with respect to the surface of the glued blanks, the gear joints can be of three types: vertical, horizontal, and diagonal. The face pressure of the fitting is set depending on the geometrical parameters of the gear joint, the cross-sectional dimensions of the workpiece and the wood to be glued. The shorter the length of the spike, the higher the pressing pressure. The main characteristic of a gear glue joint is its strength. There are two categories of relative strength: 1 - at least 75% of the strength of solid wood and Category II - at least 60%. Table 34. Standard Thorn Sizes
The assembly of spiked joints is a very important part of the process. It consists in applying glue to the side surfaces of the spikes and applying a certain pressure on the places of their pressing either immediately after applying the glue or after a certain holding. The quality of assembly of spiked joints is influenced by the following factors: the quality of surface preparation for bonding, the accuracy of the formation of tenons, the technical characteristics of the adhesive and the mode of gluing, the pressing pressure, the mode of curing of the adhesive layer. Individual spike elements have different functional purposes and differently affect the quality of the corner joint, so the requirements for the accuracy of their processing are different. The most important dimensions are the thickness of the spike and the width of the eye, since basically they determine the strength and durability of the spike connection. It should be remembered that in the spike joints of wooden parts use landing with tightness. Tension is the difference in the size of the spike and eyelet before assembly, if the thickness of the spike is larger than the size of the eyelet. When landings are formed, the tolerances of the eye and spike may be the same or different. At different tolerances of the eye and spike in the landing, it is recommended that the eye have a larger tolerance. Knots, resin pockets and a wormhole are not allowed in the spike connections and in the locations of the cutting tools and fasteners. The humidity of the exterior and vestibule doors should be 12 ± 3%, the interior door and door leaf boxes - 9 ± 3%; wood moisture for corks, slats, pins and dowels - 2-3% less wood moisture content. Bending strength should be at least 0.4 MPa for corner spike joints of doorframes and at least 0.7 MPa for strapping door panels. Door parts can be made glued in thickness, width and length. Connections with a toothed spike up to 10 mm in length are used in all parts without limiting their location, but are excluded in corner joints at distances less than 150 mm from them. The number of connections along the length should not exceed three per 1 m of the part with the minimum length of the glued blanks 250 mm; glued elements may differ in humidity by no more than 5%. No knots with a diameter greater than 5 mm are allowed in the joint zone. The knots allowed by the technical requirements for the products must be at least three different knot sizes from the base of the spikes. An extra knot is cut out - the distance from the cut to the knot is at least one knot size. When making a spike connection, you should also take into account that bonding should be done no later than 24 hours after the formation of the spiked spikes, as the spine may be disturbed due to the elastic restoration of the wood fibers. |
Popular:
New
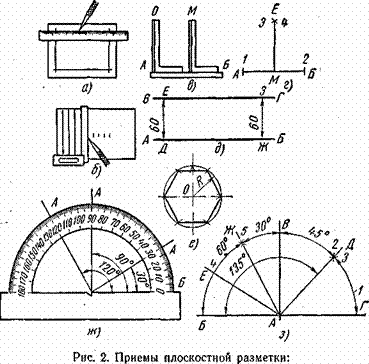
- Markup definition. Planar marking. Types of markup. Questions for self-test
- Pipe bending machines Various variations of pipe bending machine
- Safety during filing
- What should be the sharpening angle of the scriber
- Drawing on preparation of contours of future product
- Modern ways of cutting metal and its defects
- Kerner - so that the drill does not slip off!
- Objects of inanimate nature Examples of the influence of inanimate nature factors on plants
- Finishing joinery
- Block breakdown in AutoCAD - simple and effective teams from practitioners
 The most convenient way to markup is with the help of a joinery square.
The most convenient way to markup is with the help of a joinery square.  If with a narrow billet everything is simple, then for a wide billet it is necessary to make a segmented spike (for better grip). Segmented, that is, standing from several small thorns. For this we find the center
If with a narrow billet everything is simple, then for a wide billet it is necessary to make a segmented spike (for better grip). Segmented, that is, standing from several small thorns. For this we find the center  retreat to each side by 1 cm, i.e. on the shoulder, note.
retreat to each side by 1 cm, i.e. on the shoulder, note.  That's what we do. Shaded parts will be ejected.
That's what we do. Shaded parts will be ejected.  The depth of the groove should be half the stand, in this case it is 30 mm, but it should be 2-3 mm deeper in order for the glue to have a place to exit. We note the depth on the drill tape. The drill is set in the center of the workpiece.
The depth of the groove should be half the stand, in this case it is 30 mm, but it should be 2-3 mm deeper in order for the glue to have a place to exit. We note the depth on the drill tape. The drill is set in the center of the workpiece. 

 Here is a groove - using a primitive drilling-grooving device. Of course, it is not perfectly beautiful, and the edges are rounded, but it has exactly the specified dimensions and is located exactly in the center of the workpiece.
Here is a groove - using a primitive drilling-grooving device. Of course, it is not perfectly beautiful, and the edges are rounded, but it has exactly the specified dimensions and is located exactly in the center of the workpiece.  In a professional workshop, this slotting machine is used.
In a professional workshop, this slotting machine is used. 
 We turn to their preparation of the thorns themselves. Let's start with an amateur technique - sawing a spike on a circular with a carriage.
We turn to their preparation of the thorns themselves. Let's start with an amateur technique - sawing a spike on a circular with a carriage. 


 There are two ways for the spike to enter the groove. The first is to take a chisel and gouge rounding the groove
There are two ways for the spike to enter the groove. The first is to take a chisel and gouge rounding the groove  either the second option is to take a rasp and round the edges of the spike under the groove
either the second option is to take a rasp and round the edges of the spike under the groove  We make a wide preparation on a professional device - a milling cutter with a wide mill.
We make a wide preparation on a professional device - a milling cutter with a wide mill. 







 Wipe off excess glue
Wipe off excess glue  We carry out the same manipulations with a wide blank: we apply glue, we join
We carry out the same manipulations with a wide blank: we apply glue, we join 


 Summarize:
Summarize: