Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Expansion joints in buildings
- Shaber - what is it and its purpose
- Sharpening wood mills: manual work using grinding wheels and a grinding machine
- Belts and sandriks, crackers and volutes - secret codes of architecture on the example of the old Saratov Sandriki in architecture
- Surface scaling - metalwork
- Maximum load on a balcony slab: how much can a balcony withstand in a panel house?
- Projects: legend on drawings for water supply and sewage
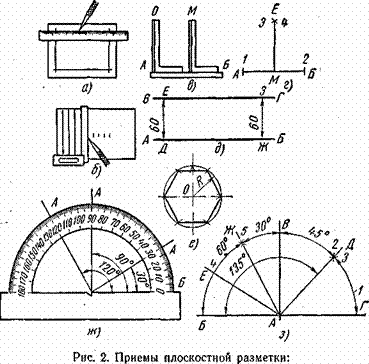
- Marking and marking parts How to mark parts with curved contours
- Slotting Tools Slotting Tools
- Mortising tools mortising tools
Advertising
| GK TechnoSpetsSnab: sale of industrial and construction equipment. Specialized lathes - design of technological processes Specialized lathes from "nevastankomash" |
|
Metal-cutting machines are machines for processing workpieces in a precisely specified size by removing the allowance layer with the formation of chips. For work, mainly abrasive or blade cutting tools are used. Machines also perform surface smoothing, rolling in rollers and other operations. Metalworking equipment allows the processing of metallic and non-metallic materials. For example, kapron, textolite, various types of plastics and wood, but special machines are intended for processing hard materials (ceramics or glass). Classification of units by groupsThe main division of the array of metal cutting machines occurs according to the technological method of processing, the method of moving mechanisms and the type of tool used. There are 10 groups of machines:
Type classificationWithin each of the 10 groups, there is a division into 10 types in accordance with the following criteria:
For example, the group of grinding and polishing machines includes round and surface grinding machines, longitudinal grinding and grinding. In the group of planing and grooving machines - longitudinally planing single-rack, transverse-planing and grooving. Within one type, there is a division into 10 sizes. The classification of metal cutting machines according to the set of technological parameters is graphically presented in the table.
Modern metal-cutting machines are manufactured with additional equipment, this speeds up the process of processing the material. Masters can increase the degree of automation in small-scale production, provided there is greater use of machines with numerical (cycle) program control (CNC). In their marking there is a letter F (C). The digital designation behind the letter indicates the type of control system:
Designation principleModels of machine tools have an original designation, in the form of a combination of letters and numbers. The following marking procedure has been established:
Machine marking The letter after the first or second digit indicates the modernization of the main parameters. Any letter that completes the marking except A, C, B, H, M, P and F shows the modification carried out with a change in the design of the nodes. The letters A, C, P, B are the designation of the accuracy class. When the tool magazine appears at the machine tool, the letter M is added. Modern types of metal cutting machines are different. For designation, F is used, but where there is a turret, it is present at the end of the marking R. Such metal-cutting machines are very popular among craftsmen. For example, the designation 2H135 indicates that it is a vertical-drilling machine of the second group, type 1, with modernization N. The maximum diameter of the drill being installed is 35 mm. Video: General information about machine toolsMetal-cutting machines produced by domestic manufacturers are divided into several categories, which are characterized by the corresponding classification. You can determine which category this or that equipment belongs to by marking it, which says a lot to those who understand it. However, no matter what category the metal-cutting device belongs to, the essence of processing on it comes down to the fact that the cutting tool and the part make forming movements, namely they determine the configuration and dimensions of the finished product. The most common types of machine tools: 1-6 - turning, 7-10 - drilling, 11-14 - milling, 15-17 - planing, 18-19 - long, 20-24 - grinding. Types of metal cutting equipmentMetal-cutting machines, depending on the purpose, are divided into nine main groups. These include the following devices:
Groups and types of machine tools (click to enlarge) In addition, metal cutting machines can be one of the following types:
Vertical milling machine - one of the representatives of an extensive milling group The classification of metal cutting machines is also carried out according to the following parameters:
Machine markingThe classification of equipment intended for the processing of metal blanks suggests that, having seen its marking, any specialist will be able to immediately tell which metal cutting machine is in front of him. This marking contains alphanumeric characters that indicate individual characteristics of the device. The first digit is the group to which the metal cutting machine belongs, the second is the type of device, its type, the third (and in some cases the fourth) is the main unit size.
After the numbers listed in the marking of the model, there may be letters that indicate whether the model of the metal cutting machine has special characteristics. These characteristics of the device may include its level of accuracy or an indication of a modification. Often in the designation of the machine the letter can be found after the first digit: this indicates that you have a modernized model, in the standard design of which any changes have been made. As an example, the marking of the 6M13P machine can be decoded. The numbers in this designation indicate that we have a milling machine ("6") of the first type ("1"), which belongs to the 3rd standard size ("3") and allows you to perform processing with increased accuracy (letter "P" ) The letter "M", present in the labeling of this device, indicates that it has undergone modernization. Automation levelsTypes of lathes, as well as devices for any other purpose, which are used in conditions of mass and large-scale production, are called aggregate. They got this name due to the fact that they are completed from the same type of units (assemblies): bed, work heads, tables, spindle units and other mechanisms. Completely different principles are used to create machines that are necessary for small-scale and single production. The design of such devices, which are highly versatile, can be completely unique.
The classification of lathes (as well as equipment of any other categories) according to the level of automation implies their division into the following types:
The most prominent representatives of metal-cutting machines are CNC devices, the operation of which is controlled by a special computer program. Such a program, which the operator enters into the machine’s memory, determines almost all the unit’s operation parameters: spindle speed, processing speed, etc.
All types of metalworking machines equipped with a CNC system contain the following typical elements in their design.
The principle of operation of metalworking machines equipped with a CNC system is simple. First, a program is written that takes into account all the requirements for processing a particular workpiece, then the operator enters it into the machine controller using a special programmer. Commands embedded in such a program are sent to the working elements of the equipment, and after their execution the machine automatically turns off. The use of metal-cutting machines equipped with numerical control allows you to perform processing with high accuracy and productivity, which is the reason for their active use to equip industrial enterprises that produce products in large batches. Due to their high level of automation, such units are perfectly integrated into large automated lines.
The main activity Group of Companies "TechnoSpetsSnab" is an salerepair and service maintenance of industrial and construction equipment. The company has been operating in the industrial equipment market since 2005, during which time thousands of private and public companies operating in various industries have become our customers. We value relationships with our customers and value the reputation earned during the activities of the company. The priority in the work of employees is an honest attitude towards partners, suppliers, customers and colleagues. That is why we work only with proven equipment from well-established manufacturers and do not sell equipment of dubious quality. For regular customers the system of discounts. Range The supplied equipment includes about 4,500 items of compressor, construction, pumping, painting, sandblasting, welding, heating, climatic equipment, power plants and machine tools. Our company sells both time-tested and inexpensive domestic equipment, as well as high-tech imported equipment from world famous manufacturers. In addition to selling equipment, our company is actively developing the direction of the sale of spare parts and consumables for compressor equipment, power plants, pumps, welding equipment, machine tools. From the availability, you can buy oils, air, fuel, oil filters, separators, as well as equipment parts that are most susceptible to wear. For equipment for which the warranty period has expired, we can offer analogues of original consumables, which can significantly reduce operating costs. Specialists of the TechnoSpetsSnab Group of Companies are ready to carry out installation and commissioning of the entire range of equipment sold. We are ready to conclude contracts for maintenance and repair of compressors, pumps, power plants, welding machines, machine tools, and thermal equipment. Work is carried out throughout Russia and neighboring countries. Specialists have many years of experience in the field of maintenance and repair of equipment and annually improve their qualifications through training from manufacturers. We provide repair services for equipment purchased in other companies. Our company is an official service center of the following manufacturers with the right to diagnose and guarantee repairs: Krasny Mayak (Yaroslavl), Bezhetsky Zavod ASO (Tver), Evan (Nizhny Novgorod), TSS (Moscow), PSM (Yaroslavl), NZGU (Novosibirsk), Robin -Subaru (Japan) Contracor (Germany) Graco (USA), Intenso (Italy), DAB (Italy), ESPA (Spain), Pressol (Germany), Wacker-Neuson (Germany), MAX (Japan) General Pipe Cleaners (USA) ), OMISA (Italy), Ballu (Russia), Hitachi (Japan), Kraftmann (Germany), Abac (Italy), Atmos (Czech Republic), Remeza (Belarus). Our company’s equipment sales offices are located in Moscow, Samara, and Saratov. The logistics service of the TechnoSpetsSnab Group of Companies will deliver equipment to your facility or construction site located anywhere in Russia and Kazakhstan as soon as possible. TO category: Process design Specialized Lathes In addition to the high-performance machines discussed above, there are still quite a large number of varieties of machines for a specific turning, which we call “specialized” machines or even “special-purpose” machines.
Fig. 1. Specialized Sundstrand Lathe. These machines are created by companies either for parts that, due to their shape or the required degree of accuracy, cannot be quickly and cost-effectively processed on the described types of machines, or to obtain particularly high productivity, or to achieve the concentration of a large number of operations on one machine. In fig. 1 shows a specialized machine tool from Sundstrand Mch. Co for turning both flanges of the rear axle housing. We have, in this case, a turning center machine with the following major modifications: Machine control is reduced to changing the part and putting the machine into operation. For a clearer picture of this operation, we give a few more detailed data: Sizes: diameter of flanges - 5 ", detail length - 53" In fig. 3 shows the same machine on the turning of both ends of the axle shaft. The drive is also implemented as in the previous treatment (due to its rigid structure it serves at the same time as a lunette). Two front calipers produce longitudinal turning of all diameters, including the cone (a copying device). Two rear calipers with wide shaped cutters give the final profile to both ends of the axle shaft. The following data can be provided about this operation: The use of specialized multi-cutters can also be seen on the turning of the camshafts of a car engine This processing is usually performed in 2 or 3 operations on special multi-cutters with 2 or 3 long calipers, most often located on one side, on which the required number of cutters is installed (up to 24 or more).
Fig. 3. Turning the axis on the SundstrMd machine.
Fig. 4. Lo-Su’ing machine - for turning cam rollers (specialized). In order to avoid deflection of the roller from the pressure of the cutters, it is supported by one or more lunettes. This treatment is often carried out in well-equipped mills on Seneca Falls Mach's specialized Bo-Swing machines. Co or, for large-scale production, on elongated Fay Automatic Lathe machines. The latter machines, in view of the whole range of available devices, can also be considered specialized for the aforementioned processing.
Fig. 5. Cutting the necks of the cam roller on the Lo-Swing machine. In Germany, Haiden-riech & Harbeck builds machines for this purpose. In fig. 5 shows a nerve operation (trimming) of turning a camshaft on a Lo Swing machine. The cam roller is supported during turning by two lunettes (from the side opposite to the incisors). Therefore, before this operation, in addition to facing and centering, two necks of the shaft bearings must be machined, on which the rollers of the lunettes should rest. Specialized multi-tooling for turning a camshaft differs from conventional multi-cutter tools with a longer bed, small height of centers, length, location and number of supports, arrangement of lunettes and, consequently, more power due to the large number of simultaneously working cutters. One of the signs of the classification of machines is their degree of universality. It characterizes the variety of parts and operations for which the machine is suitable. The greater this diversity, the greater the technological capabilities of the machine. From this point of view, all machines are divided into 4 groups: General purpose machines (widely-universal) - screw-cutting, vertical and horizontal milling, vertical and radial drilling, circular grinding, etc. General purpose machines with increased productivity - turning-revolving, turning automatic machines and semiautomatic devices, longitudinally and rotary-milling, centerless grinding, etc. (less versatile, have a smaller range of rotational speeds and feeds). Special machines - to perform only one operation in a single process. Special machines are divided into two types: ordinary special and aggregate. The most widely used aggregation for machine tools drilling and boring groups. In some cases, a special machine is created by upgrading any machine of another group, then they are called specialized. For example, it turns a lathe into a copy-milling machine (for machining the blade blade of a gas turbine engine), etc. In ENIMS, a modern classification of machine tools has been developed. As the defining parameters of the classification, taken the detailed and target specialization, as well as the degree of automation of the equipment. When describing the detailed specialization of systems, it is considered expedient to use the above terminology. According to the degree of automation, machines are divided into automatic, automated and non-automated. In addition, the machines are further divided into single-purpose and multi-purpose (this term appeared together with CNC machines). The following classification criteria is the accuracy of the machines: Technological processes are being developed both in the design of new workshops and factories, and for existing workshops. In the first case, focus on the latest machine tools. In the second - develop TP taking into account the available equipment.
The range of machine quality indicators in GOST 4.93-83 is more fully described. Machine tools depending on the type of treatment , divided into nine groups, and each group - into ten types (subgroups), characterizing the purpose of machines, their layout, degree of automation or the type of tool used. Group 4 is designed for EDM, ultrasonic and other machines. The designation of the machine model consists of a combination of three or four numbers and letters. The first digit indicates the group number, the second number of the subgroup (machine type), and the last one or two digits are the most characteristic technological parameters of the machine. For example:
The letter after the first digit indicates the different versions and upgrades of the basic basic model of the machine. The letter at the end of the digital part means the modification of the base model, the accuracy class of the machine or its features. The following indexing of machine tool models with program control is adopted:
Special and specialized machines are designated by the letter index (of one or two letters) assigned to each plant, with the model number of the machine. For example, mod. MSH-245 - semiautomatic reysoshiruyushchy of the increased accuracy of the Moscow factory of grinding machines |
||||
Popular:
New
- Markup definition. Planar marking. Types of markup. Questions for self-test
- Pipe bending machines Various variations of pipe bending machine
- Safety during filing
- What should be the sharpening angle of the scriber
- Drawing on preparation of contours of future product
- Modern ways of cutting metal and its defects
- Kerner - so that the drill does not slip off!
- Objects of inanimate nature Examples of the influence of inanimate nature factors on plants
- Finishing joinery
- Block breakdown in AutoCAD - simple and effective teams from practitioners