Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Expansion joints in buildings
- Chaber - what is it and its purpose
- Sharpening wood cutters: manual work, using grinding wheels and a grinding machine
- Belts and sandriks, crackers and volutes - secret codes of architecture on the example of the old Saratov Sandriks in architecture
- Surface grit - tooling work
- Maximum load on the balcony slab: how much can a balcony withstand in a panel house?
- Projects: symbols on drawings for water supply and sewage
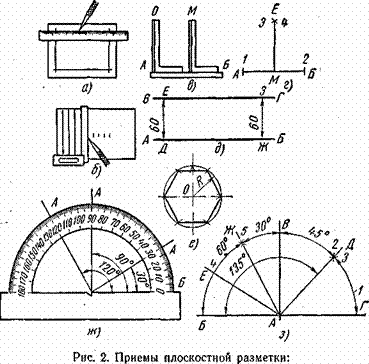
- Marking and marking details How to mark the details with curved contours
- Tools for slotting Tools for slotting
- Tools for chiseling Slotting tools
Advertising
| Safety in the production of stone work. Safety in the performance of stone work. Safety in the production of stone work |
24
25
26
27
28
29
..7. SAFETY AND SAFETY PROTECTION IN PRODUCTION OF STONE WORKS7.1.Safety techniques for brickworkSafety- This is a complex of measures and rules, with the exact observance of which safe working conditions for life and health are provided. Before workthe bricklayer needs to receive instructions on safe methods and techniques for performing the production task; inspect the workplace and check the correct placement of materials; check the serviceability of the tool, inventory, fixtures; establish the presence of external protective visors and fences in the openings; Wear protective clothing and a hard hat. When laying with scaffolding or scaffolding(Fig. 7.1) the following requirements should be met: 1) the working flooring should be located 150 mm below the top of the masonry; 2) the width of the flooring should be at least 2 m, and the flooring itself should have a flat surface and not sag when walking; 3) the gap between the masonry and the flooring should not exceed 50 mm; 4) with a floor height of not more than 1 m of the scaffold and the forest must be 5) when placing masonry materials along the laid out wall, there should be a passage of at least 60 ... 70 cm. Fig. 7.1. Storage of masonry materials
Wall materials on pallets with hooks on the ends are served with a gripping-case with a rigid fence. The end brackets, hingedly connected to the grip frame, are hooked over the four hooks of the sling and are fed to the pan at the mason’s workplace (Fig. 7.3). Brick coming inconstruction site without pallets, served self-lockingcapture (Fig. 7.4 and 7.5).The weight of the package with the grip is 1.9 tons, therefore it is allowed to install a brick with such a grip only on reinforced scaffolding. If the scaffolding and the scaffolding are not designed for such a load, then the grab lifts first six upper rows of the package, then four lower ones.
Fig. 7.3. Submission of bricks on pallets with hooks-gripping case: but- putting cases on the pallet; b- fixing the fence for the pallet hooks; 1 - hooks of the pallet; 2 - case body; 3 - rigid fence
Fig. 7.4. Self-engaging feed
Fig. 7.5. Feed mortar: The solution is fed by a dispensing hopper moved by a crane (Fig. 7.5). In the workplace, masons' boxes are filled with mortar from a bunker, the volume of which allows you to fill up to five mortar boxes. The boxes loaded with solution serve on a workplace. When submitting masonry materials it is forbidden to be under the supplied load. Arrangement of materials on the working flooring scaffolding and scaffolding, as well as on the floors are carried out in accordance with the scheme approved by the project of work. In the process of layingthe mason observes the following security measures (fig. 7.6): - monitors the health of hand tools, the working surfaces of which should be smooth, and wooden handles tightly mounted and wedged; - works in mittens; - performs the jointing of external seams after each row so as not to be on the wall; - performs the cutting and brick hemming in protective glasses; - protects laid openings or inserts window or door blocks into them; - laying in the level of floors completes in the form of a ledge (rim), rising to 150 mm above the overlaid floor; - when laying out external pilasters when it is necessary to stand on wall, puts on a safety belt and is fixed to the stable parts of the building.
Fig. 7.6. Security measures for masonry: but- fencing openings; Safety in the production of earthworks Safety arrangements Prior to the commencement of earthworks at the locations of existing underground utilities, arrangements for safe working conditions should be developed and agreed with the organizations operating these communications, and their location on the ground should be indicated: Work in the area of existing communications to be carried out under the guidance of a foreman or master, and in the protection zone of cables under voltage and gas pipelines under the supervision of representatives of these farms; Upon detection of explosive materials, earthworks should be stopped until permission from the relevant authorities is obtained; When working on sites with possible contamination of the soil (landfill, cemeteries, cattle cemeteries), obtain permission from the State Sanitary Inspectorate; When working in settlements where people move, trenches and trenches should be protected with protective fences that are at night; The places of passage of people through the trenches should be equipped with transition bridges, lit at night; The soil extracted from the pit or trench should be placed at a distance of at least 0.5 m from the recess edge; It is forbidden to develop soil "undermining"; Digging trenches and trenches with vertical walls without fasteners is allowed to a depth of no more than: 1 m - in bulk, sandy, coarse soils; 1.25 m - in the sandy; 1.50 m - in loams and clays. Digging of pits and trenches with a slope without fastenings in non-rocky soils above the groundwater level is allowed with a depth of excavation and steepness of slopes according to tab.4 (SNiP-4-80); The steepness of the slopes of the grooves with a depth of more than 5 m should be established by the project; When installing fasteners, their upper part should protrude over a notch of not less than 15 cm. Install fasteners from top to bottom as you develop a notch to a depth of no more than 0.5 m. Disassembly should be done in the bottom-up direction as the backfill of the excavation takes place; Before admitting workers to trenches and trenches with a depth of more than 1.3 m, the stability of slopes or wall fixings should be checked. 1. When moving and feeding brick, ceramic stones and small blocks to a workplace, pallets, containers and load handling devices should be used to prevent the load from falling when lifting and moving the load at height. 2. The level of masonry after each movement of scaffolding should be not less than 0.7m above the level of the working floor or overlap. 3. When laying walls with a height of more than 7m, it is necessary to use protective visors around the perimeter of the building that meet the following requirements: The width of the visor should be at least 1.5m and should be installed with a slope of 110 degrees to the wall, and the gap between the wall of the building and the surface of the visor should not exceed 50mm. Protective peaks must withstand evenly distributed snow load. The first row of protective visors should have solid flooring at a height of not more than 6m from the ground and be maintained until the completion of masonry walls. 4. Workers engaged in the installation, cleaning or removal of protective visors should work with safety belts. Walk on the visor, use them as scaffolding, and also store materials on them is not allowed. All tools and fixtures must be used in accordance with their purpose. Before work, make sure that the tools are intact: correctly and firmly mounted on the handles, the working surfaces of the tools are flat, without burrs; damaged or deformed tools cannot be used. The bricklayer must work in mittens to protect the skin from abrasion. Brickwork is performed from the overlapping of the scaffolding or scaffolding. Scaffolding and scaffolding installed on cleaned, aligned surface. Special attention is paid to ensure that the stands of tubular scaffolding are properly installed on the ground, the ground must be tightly tamped. Do not install racks on the ground, not cleared of snow and ice. For uniform distribution of pressure under the rack, wooden linings are laid perpendicular to the wall being erected (one lining for two racks). Scaffolding and scaffolding cannot be overloaded with materials beyond the scaffolding established for a given construction or scaffold of design load. Concentration of materials in one place should be avoided. Materials are laid so that they do not interfere with the passage of workers and transportation of materials. Between the piles of materials and the wall leave a working passage width of at least 60 cm. Decking from inventory shields stitched with slats on scaffolding and scaffolding should be smooth and without cracks. The gap between the wall of the building under construction and the working floor of the scaffolding should not exceed 5 cm. This gap is needed so that, by lowering the plumb boom below the scaffolding, one can check the verticality of the erected masonry. All decks of scaffolding and scaffolding with a height of more than 1.1 m, with the exception of scaffolding of continuous mashing, are protected with a handrail at least 1.1 m high, consisting of racks and attached to them from the inner side (at least three) of horizontal elements: side board 150 height mm, installed close to the flooring, intermediate element and handrail. If the handrail is made of board, it must be touched. The board is placed in order to prevent any objects from falling from the scaffolding. For lifting workers on the scaffolding install ladders with fences (railings). The condition of the forests and scaffoldings (connections, fixtures, flooring and fences) is established by systematic observation. Every day after the end of the work, the scaffolds are cleared of debris and before the start of the shift they are checked by the foreman, who supervises the relevant area of work on this object, and the foreman. The brick is raised to the floors (scaffolding, scaffolding), as a rule, by packages on pallets with the help of cases preventing bricks from falling out. It is allowed to lift bricks in containers and packages without pallets only with the help of safety grippers (subject to the use of devices protecting the bag). Devices for lifting bricks (cases, grips) must have devices that prevent spontaneous opening of these devices during lifting. It is forbidden to dump empty cases, grabs, pallets from floors; they are lowered by a crane. Laying of any tier of the walls is performed so that the level of it after each rewinding of the scaffolding is 70 cm above the level of the working floor or floor. Below this level, bricklayers work in safety belts, which are attached to structures, or the perimeter of masonry is protected with protective nets. Do not leave materials, tools, debris on the walls, as they may fall on people below. In the course of laying in the openings of the walls install window and door blocks or inventory fencing. Eaves protruding beyond the wall surface by more than 30 cm are laid out from external scaffoldings or from inventory exhaust platforms, the flooring width of which should be 60 cm more than the width of the eaves. At the same time, the materials are located on the inner floorings, and the bricklayers work while they are on the final forests. Fig. 66. Bracket for the device of protective visors:
When laying walls with a height of more than 7 m around the perimeter of the building, arrange outdoor inventory protective visors in the form of flooring on brackets (Fig. 66). The brackets are hung on steel hooks 2, embedded in the masonry as it is erected. The width of the visor is not less than 1.5 m, the external angle of elevation is 20 °. When constructing visors, the following requirements are met: the first row of visors is installed at a height of not more than 6 m from the ground and left until the erection of the wall masonry to the full height; the second, made solid or of mesh materials with a cell of no more than 50x50 mm, is at a height of 6 ... 7 m above the first, and then is moved every 6 ... 7 m along the laying. The workers install protective covers in safety belts. It is forbidden to walk on the visors, as well as use them as scaffolding and for folding materials. Without protective visors, you can lay the walls of buildings with a height of not more than 7 m, but on the ground along the perimeter of the building they arrange fences at a distance of at least 1.5 m from the wall. When laying walls with internal scaffolding above the entrances to the stairwells, arrange permanent canopies of at least 2x2 m in size. It is forbidden to lay out walls with a height of more than two floors without the device of intermediate floors or temporary flooring on the beams of these floors, and also without the device in the stairwells of platforms, marches and their fences. The seams are embroidered from floors or from scaffolding after laying each row. During this operation it is forbidden to be on the wall. test questions
When performing stone work should be provided measures to prevent workers from hazardous and harmful production factors such as: a) the location of the workplace at a height; b) moving machines and mechanisms; c) moving structures; d) collapsing structures; e) neuropsychic loads associated with the monotony of labor. When laying the walls of the building to a height of 0.7 m from the working floor and the distance from the level of the masonry from the outside of the wall to the ground (floor) more than 1.3 m, it is necessary to use fencing devices, and if it is impossible to use them, safety belts. It is not allowed to lay the walls of the subsequent floor without installing supporting structures for the floor, as well as platforms and marches in the stairwells. The maximum height of the construction of free-standing stone walls (without laying the floor) must be determined in the design of the work. Laying of external walls up to 0.75 m thick while standing on a wall is not allowed. When the wall thickness is more than 0.75 m, it is allowed to make laying from the wall using a safety belt attached to a special safety device. It is allowed to remove temporary fastenings of elements of the cornice, as well as the formwork of brick lintels after the mortar reaches the strength established by the project. When moving and feeding bricks, small blocks, etc. materials for workplaces with the use of lifting equipment should use pallets, containers and lifting devices, excluding the fall of the cargo. 8.5. Safety requirement when performing installation work. Installation of building structures relates to work with increased danger. Workers performing installation work must undergo a medical examination, special training, pass an examination and receive a certificate of entitlement to perform work. Lifting machines and rigging devices prior to commencement of work and during operation must undergo a technical examination in accordance with the requirements of Gosgortekhnadzor. Inspection of lifting machines and mechanisms produced monthly. Traverses inspect at least once every 6 months, ticks - after 1 month, slings - every 10 days. External examination of steel ropes should be carried out daily, guided by the norms of rejection of worn ropes. The rigging devices under examination are tested with a load that exceeds by 25% the calculated carrying capacity. The test date and load capacity are indicated on tags attached to the gripping devices. Cranes should be installed in accordance with the design of the work, it is necessary to ensure safe distances of cranes from power lines, slopes of pits, dimensions of buildings and structures. Scaffolding and scaffolding should have barriers at the workplace level of at least 1 m. Typical inventory scaffolding and scaffolding are used for installation works. Scaffolding and lifting platforms must have manufacturer's passports. Installation of structures produced in accordance with the project of work. It should include basic safety measures. Slinging structures produced by slings or special lifting devices according to the schemes provided by the flow chart, using semi-automatic devices for raspropovka from the ground. With free installation, raised elements must be kept from swaying with braces. Structures that do not have sufficient rigidity must be strengthened according to the project. Rasstropovka mounted elements produced only after secure. Before final consolidation, their stability should be ensured by means of temporary connections, braces, conductors, etc. It is forbidden to combine installation work on the same grab vertically with other work in the lower floors with a building height of less than five floors. It is possible to combine these works only in exceptional cases. Installers must be outside the contour of the installed structures from the opposite side of their flow. Assembly operations at height are carried out with special scaffolding or cradles. Mount climbers should have special clothing, non-slip shoes and safety belts. To move from one structure to another, ladders, transition bridges and ladders should be provided. The site where the installation is carried out is a dangerous area and it is forbidden to be on it. The boundary of the danger zone is determined by a circle delineated by a radius equal to the reach of the crane’s boom hook, plus 7–10 from the contour of the lifted load (the load can fly at a distance of 7 m to a height of 100 m to a distance of 7 m ). Only one person should lead the lifting of structures - the foreman of the assembly team or a link one. The “Stop” command can be submitted by each worker who has noticed the danger. Installation work is prohibited when the wind has a force of 6 points (10 -12 m / s) and more at height, in open places, with icy conditions, heavy snow and rain. When using tower cranes, the latter should be carefully secured. Before the start of installation work, systematically inspect the ropes and slings used. Ropes with dangling wires one twist pitch in more than 10% with a cross and 5% | with a one-sided twist, must be removed from use. All gripping devices prior to use are tested and tagged with an indication of the permissible carrying capacity. Test results are recorded in special journals. Before lifting the elements, the installer is obliged to carefully inspect the condition of the mounting hinges, gripping devices, correctness of slinging. It is not allowed to lift with a crane loads frozen to the ground, covered with soil, cluttered with other elements. When mounting structures approach them and begin installation in the design position is possible only after the element is lowered at a distance of no more than 30 cm from the installation site. During breaks in work it is forbidden to leave the load hanging on the crane hook. The most dangerous are the work at heights. Climbing consider work that perform at a height of more than 5 m from the surface of the soil or working flooring. Working at height installers must use helmets, safety belts, non-slip shoes. Carbines safety belts fasten to the resistant elements or specially stretched ropes. All installation work at height is carried out with scaffolding, designed for the load from people, tools and auxiliary materials. Safety in the production of earthworksIn addition to general excavation works, special safety requirements must be observed. Near underground utilities, earthworks should be carried out manually or with mechanized tools only under the supervision of a foreman. In those cases when such communications as gas pipelines and electric cables are in force, the presence of gas or energy workers is obligatory during the excavation work. If any work that is not indicated in the communications documentation is found at the place of production, the work should be immediately terminated before obtaining the official permission of the respective organization. The limiting depths of pits and trenches in dry soils and near existing structures should not exceed the values given in the regulatory documents. In the process of the excavator, people can not be at a distance less than its zone of action plus 5 m. The soil is loaded into vehicles from the side of its rear and side walls. Safety in the production of stone workOne of the main conditions for the safe conduct of work is the proper organization of the workplace of a bricklayer and his work. Before starting work, the bricklayer must: inspect the workplace, make sure that the placement of masonry materials is in order, that the tools, equipment, tools, and tools are in good condition, and that the installed scaffolding or scaffolding is stable. Mason should work in mittens that protect the skin of the hands. Scaffolding and scaffolding is installed on cleaned, leveled surfaces. All other elements of forests should be designed for strength, and forests in general - for sustainability. Racks of scaffolding at all heights are attached to strong parts of a building or structure. If the attachment of scaffolding to structures erected is impossible, their stability is ensured in another way (for example, they put braces and stretch marks). Places and methods of attachment should be specified in the PPR (project work). It is forbidden to fasten forests to parapets, cornices, balconies and other protruding parts of buildings and structures. Scaffolding and scaffolding can not be overloaded with materials in excess of the design load established for the scaffolding or scaffolding. Avoid the accumulation of materials in one place. Every day, after work is finished, the scaffolding and scaffolding are cleared from debris. There is a gap between the working floor and the wall of the building under construction, but its size should not exceed 5 cm. Every day before the start of the shift, the master in charge of the relevant area of work and the foreman of the SSO should check the condition of the scaffolding and scaffolding. Masonry with a height of more than two floors is prohibited if there are no interfloor overlaps. The laying of any tier of the walls is carried out in such a way that its level after each movement of the scaffolding is 15 cm above the working floor (the mason must not work with a dangerous slope). In the course of the work, special attention should be paid to ensuring the stability of the structures (at the stage of their incomplete construction). Laying out the walls of the next floor is allowed only after installation of floor structures. The maximum height of the erection of a free-standing stone wall without temporary fixing should not exceed the values established by the SNiP depending on the wall thickness, the bulk density of masonry and the magnitude of the velocity head of the wind or wind speed. The laying of walls at the level of overlap, arranged from precast concrete slabs, is performed from the scaffolds of the underlying floor. In cases where, in the process of laying, wooden and window openings are not filled with ready-made blocks, inventory fences are installed in the openings. Wall materials, tools or debris must not be left on the walls during work breaks. Cornices protruding from the plane of the wall by more than 30 cm should be made from external scaffolding or from inventory scaffolding, the width of the flooring, which should overlap the eaves by 60 cm. At the same time, the materials are located on the inner floorings, and the bricklayers work while they are on the final forests. When laying walls with internal scaffolding around the perimeter of the building, arrange outdoor inventory protective visors in the form of wooden flooring (or mesh made of synthetic materials) on the brackets. The first row of visors is installed at a height of not more than 6 m from the ground and, prior to the erection of the construction, the masonry of the walls is full height; The second row of visors is placed at a height of 6-7 m above the first, and then during the laying they rearrange it every 6-7m. Without protective canopies, it is possible to lay the walls of buildings with a height not exceeding 7 m, but on the ground along the perimeter of the building they arrange a fence at least 1.5 m from the wall. When laying walls with internal scaffolding above the entrance to the stairwells, arrange permanent canopies of at least 2x2 m in size. Staircases and marches, as well as openings in the ceilings protect. Brick is raised to the floors (scaffolding, scaffolding), as a rule, by packages on pallets with the help of cases preventing bricks falling out, or by grippers in the presence of devices protecting the package. Empty cases, grabs, pallets dipped crane. |
Popular:
New
- Markup definition. Planar marking. Types of markup. Questions for self-test
- Pipe bending machines Various variations of pipe bending machine
- Safety during filing
- What should be the sharpening angle of the scriber
- Drawing on preparation of contours of future product
- Modern ways of cutting metal and its defects
- Kerner - so that the drill does not slip off!
- Objects of inanimate nature Examples of the influence of inanimate nature factors on plants
- Finishing joinery
- Block breakdown in AutoCAD - simple and effective teams from practitioners
 Brick and mortar feed. Ceramic brick, stone on pallets with supporting bars at the workplace of a bricklayer are served with a grab-case consisting of two L-shaped half-cases with gripping levers that are brought under the pallet board (Fig. 7.2).
Brick and mortar feed. Ceramic brick, stone on pallets with supporting bars at the workplace of a bricklayer are served with a grab-case consisting of two L-shaped half-cases with gripping levers that are brought under the pallet board (Fig. 7.2).