Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Expansion joints in buildings
- Chaber - what is it and its purpose
- Sharpening wood cutters: manual work, using grinding wheels and a grinding machine
- Belts and sandriks, crackers and volutes - secret codes of architecture on the example of the old Saratov Sandriks in architecture
- Surface grit - tooling work
- Maximum load on the balcony slab: how much can a balcony withstand in a panel house?
- Projects: symbols on drawings for water supply and sewage
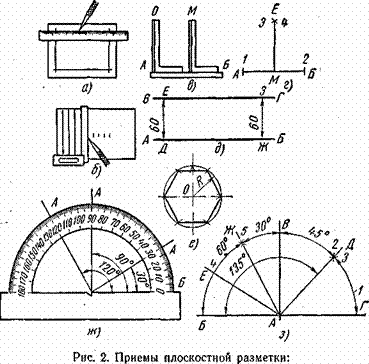
- Marking and marking details How to mark the details with curved contours
- Tools for slotting Tools for slotting
- Tools for chiseling Slotting tools
Advertising
| Public insects bees and ants are useful insects. §28. Public insects - bees and ants. Beneficial insects. Insect protection. V. Homework |
|
Insects living in large families are called social. Family members of social insects are divided into two groups: males and females, which perform the function of reproduction, and workers, do not participate in reproduction, but jointly perform all work on maintaining family life and protect individuals of the first group. Only representatives of two rows form families: Hymenoptera and Termites. The Hymenoptera series unites insects with complete transformation, which have two pairs of transparent wings that are fused together (Fig. 69). Another feature of Hymenoptera is that males are born only from unfertilized eggs. A number of Hymenoptera has about 90,000 insect species. Developed hymenoptera - stinging insects: wasps, bees, ants. They all care about their offspring. Wasps are both social and solitary insects. They feed the larvae with animal food, which is harvested by paralyzing their victims with the help of the stinger. Adult wasps feed on the nectar of plants or aphids. They build nests from a kind of semi-finished paper: with their jaws they gnaw off small fibers of wood, moisten them with saliva and fray. The life cycle of the family of forest wasps, common in the forests of Ukraine, such. In the spring from the store - some kind of crack in the wood - the female takes off. In a convenient location, it arranges a nest hanging from the ceiling of the vault and consists of several cells. In each cell the female lays on the egg, from which the larva appears. The female feeds the larvae chewed by insects. She brings them food like a bird, feeding the chicks. The larvae pupate, and after the stage the pupae turn into workers. Now they arrange nests themselves and take care of new larvae. In addition, the workers feed the female, whose only duty is to lay eggs. Workers are also females, but they do not participate in the breeding process. Externally, female workers do not differ from the female queen and, after her death, are capable of laying eggs themselves. During the summer, the number of individuals in the nest increases, the family increases. At the end of summer, not working eggs appear from the eggs, but full-fledged females and males mate. Then the males die, and the females hide until spring. With the onset of winter in the nest, “a real tragedy is played out”: the old female and the workers kill all the larvae and pupae, did not have time to develop, and then they themselves die. Hornets are big wasps that sting very painfully. They build their nest in the hollows of trees. As a building material for the nest, it is not wood that is used, but the bark of young birch branches. The larvae are fed by insects, including honeybees. Bees The honeybee is one of the few insect species that humans cultivated (Fig. 70). The bee family consists of a queen (queen), workers (underdeveloped females, which, unlike wasps, are not capable of reproduction) and male drones. After mating, drones are not allowed into the hives, so they die or the worker bees kill them. Bee larvae develop in wax cells from which the bees build special rows - honeycombs. Do you know that to produce 1 kg of honey, a bee brings 150,000 portions of nectar from 100,000,000 flowers into a hive, overcoming the distance to 300,000 km? This is enough to go around the globe 5 times at the equator. Young worker bees perform a variety of work: they clean the cells of the combs, feed the larvae, the uterus, build honeycombs, and then begin to collect pollen and nectar from flowers. In new places, bees move families, called swarms, and consist of a queen and workers. Bees are very useful insects. First, they give honey - a tasty and nutritious product. Secondly, wax is obtained from comb, which is used for the manufacture of varnishes and paints, as well as in the electrical industry. Thirdly, these insects produce bee glue, or propolis, which has an antimicrobial effect, promotes healing of wounds. The composition of the propolis resinous substances, wax, pollen, etc .. Bees use propolis to gloss over the cracks in the walls of the hives, and the man - in medicine. However, the most important thing is that bees pollinate plants. Bumblebees are, in fact, big bees. They lead a social lifestyle. They build their nests in secluded places. In early spring, single females fly low above the ground, looking for a place to found a new family — a slot or some kind of burrow in the ground. The bumblebee nest is spherical and consists of several cells. In one cell, the larvae develop, while others contain stocks of honey. The development of larvae lasts 20 days. Individual pupils emerge from the pupae, much smaller in size than the uterus. After the death of the queen, the workers are able to multiply. Bumblebees are one of the most vulnerable groups of insects. In many European countries for catching only one bumblebee is charged a large fine. However, despite security measures, many species of these useful furry insects resembling teddy bears have almost disappeared. Of the 38 species of bumblebees living in our country, 10 species need special protection. Do you know that in the insect world there are bumblebees, “cuckoos” laying eggs in the free cells of the nests of other species of bumblebees? Since all the bumblebees are very similar, the nest owners treat the larvae that have emerged from alien eggs as if they were their own. Termites lend to insects with incomplete metamorphosis. By way of life and features of the external structure, they are similar to ants, they are often called “white ants”. Termites live in numerous families in the soil or wood and almost do not appear on the surface. They construct huge cone-shaped buildings, similar to anthills, where millions of individuals live. Termite colonies consist of winged males, queen (queen) and workers. The largest individual workers become soldiers, they have strong jaws, so their purpose is to guard the nest. The rest of the workers produce food for the soldiers and the womb, who are not able to feed themselves. Only males and queens can fly, but after the summer of males, the males die, and the fertilized female loses its wings and starts laying eggs. On the territory of Ukraine in the steppe zone live termites of only one type - termites photophobia. Social insects form families consisting of males and females, capable of breeding, and individuals-workers who serve them. Such a distribution of individuals in function is a special phenomenon in the animal world. Check yourself. 1. Which insects are called solitary, and which are called social? 2. What are the distinguishing features of Hymenoptera? 3. Describe the life cycle of a forest wasp family. 4. How does the life of a bee family differ from the life of a family of wasps? 5. How is the ant family formed? Some types of insects domesticated by man and are of great industrial importance. This is, for example, a honey bee. She lives everywhere where flowering plants are found. Bees – social insects living in large families, including up to 80 thousand individuals. Family members share food with each other, take care of their offspring together, protect their home. They can not live separately from each other. Family of bees called digging. Wild bees live in hollows of trees, domesticated - in beehives. The honeybee nest is a vertical row of cells - honeycombbuilt from wax. The cells vary in size. The stock of feed is stored in them, the posterity grows.
In bees, as well as in all other social insects, well pronounced polymorphism (or variety) those. external differences depending on the functions performed in the family. Honeybee family includes one large female (womb, or queen), about 300 males (or drones) and tens of thousands of worker bees (barren females)unable to breed.
Uterus - the largest and most important bee in the family. The actions of the many thousands of community are harmonious and organized, but if the uterus dies, the family turns into a cluster of helpless, randomly running insects. It has dimensions of about 2 centimeters, a long abdomen, in which the genitals are strongly developed. The main function of the uterus - daily in warm time, lay up to 2 - 3 thousand eggs. The uterus lives five to six years. In the summer in the family appear drones. They are medium in size and very large, touching the back of the head. T the runners do not work, do not protect the family, since they have no sting and do not procure food on their own. Their only meaning is participation in breeding. Worker bees have, in comparison with the uterus and drones, smaller sizes. The head of a working bee is large, covered with hairs, there are two faceted eyes and three simple eyes between them. They build honeycombscontaining larvae, find and collect nectar, protect with a sting dwelling, do all the work in the nest. Larvae and pupae develop in honeycombs, honey and perga (pollen processed by bees) are stored. On the head of the bees are antennae. The organs of sight and smell allow bees to look for honey plants and to do all the work in the hive. Mouth apparatus of bees gnawing-licking. The upper jaws allow you to process the wax when building honeycombs. Proboscisformed by the lower lip, serves to lick nectar. Nectar enters the goiter, where it mixes with the secretions of the salivary glands. With this mixture, the bee fills the cells of the honeycomb, where the mixture turns into honey.
To collect pollen bees use limbs. On the back of the pair of legs from the outside there is a smooth area surrounded by hairs, - basket. The first, extended segment of the hind paws is internally covered with rows of hairs and forms brush. These are the collecting limbs of bees.
The bee brushes the body with a brush, collects pollen after visiting flowers, then rubs a limb on a limb, forming a ball of pollen, the so-called a curbwhich moves to the basket and transfers to the hive.
On the abdomen of the worker bees are waxy glands. The small wax plates formed by them stand out on smooth parts of the abdomen - mirrorsand then removed by the hind limbs, stretching the jaws and used for the construction of honeycombs.
Consider how it happens breeding and development of bees. A fertilized uterus and worker bees winter in the hive, which completed their development at the end of the previous summer. Spring uter postpones two types of eggs: in large cells of honeycombs - unfertilized eggs, in small - fertilized. Drones develop from unfertilized eggs, from fertilized - working bees and a new queen.
Of eggswhite worm-shaped leaves maggots. The larvae grow rapidly, grow in size, and then about puppet. Before pupation of the larvae, worker bees seal the cells with wax. Insects emerged from the pupae gnaw through the lids and go to the honeycomb. During the breeding season, a large number of worker bees first appear, then drones and a young queen. With the release of the young uterus begins swarming or mating flight of insects. The old queen and part of the worker bees fly out of the hive and find a suitable place to found a new family. After the old uterus has left the hive, one of the drones mates in the air with the young uterus and dies; the rest of the drones will not be allowed into the hive, and those will die of starvation. The fertilized young queen returns to the hive and starts laying eggs. Beekeeping - one of the important areas of national economy. Bees give a person a valuable food product - honeywhich is important healing properties. Man uses beeswax, royal jelly (the secret of the salivary glands of bees), bee venom and bee glue (propolis) for the manufacture of drugs. But the main role of the bees is plant pollination. Another domesticated insect species is silkworm. It was first domesticated in China about 5 thousand years ago, and then spread throughout the world.
Silkworm moths have a thick whitish body, completely covered with hairs. They have two pairs of wings, but unable to fly. In the oral apparatus they do not have a proboscis, therefore, they don't eat. Therefore, they live a short time: die soon after laying eggs. Females lay between 300 and 600 eggs, called grenoy. Caterpillars leave eggs - " silkworms". They actively feed on mulberry leaves. Caterpillars contain and feed on special racks. They develop about 40 days, pass molting. During pupation, the caterpillar emits silky and forms a cocoon around itself. Silk is secreted by a pair of modified salivary glands, which are called spinning or silk-separating. In the air, secretions of the glands quickly harden and form a strong thread, the length of which in a cocoon reaches one thousand meters. Silk thread used for the production of silk fabrics, in medicine - for stitching wounds.
Sericulture - The branch of agriculture engaged in the cultivation of the silkworm to obtain silk. Another one of the beneficial insects are ants. They live in large families. They have body sizes from one centimeter to three. There are about 10 thousand species of ants. Red Forest Ant has a red-brown color, lives in the forest and builds high anthills.
Black garden antIt builds small hillocks in open places (meadows and glades). It can be found in the cracks of the walls of wooden houses, in the hollows and stumps of old trees. In the houses there is a house ant, reaching a length of 5 millimeters. In most species of ants, the sting and poisonous glands are well developed, emitting formic acid.
The family of red forest ants includes winged males and females, and wingless working ants. Young males and females are winged; they are larger than working ants.
From early spring, working ants take care of the offspring, produce food for the larvae and queens, repair and finish the anthill, and protect it from enemies. Anthill - a complex structure with aboveground and underground parts, a complex system of galleries and chambers in which eggs, larvae and pupae of ants can be found. Ants overwinter in the underground part of the anthill.
In warm autumn days, matings of males and females take place. After fertilization, the males die, and the females break off their wings and, finding a suitable place, begin to build a new anthill. Ants are beneficial insects. They destroy harmful insects that damage the leaves of plants. It is estimated that a family of red forest ants delivers about one kilogram of insects to an anthill per day. Making moves in the soil, the ants loosen it, provide ventilation, hydration and enrichment with humus. Beneficial insects include dragonflies, ladybugs, ground beetles . Dragonflies hunt in flight and destroy mosquitoes, midges and other blood-sucking insects. ladybugs eat aphids and their larvae. Ground beetles also eat a large number of harmful insects, mollusks. Grave beetles and carrion eaters they bury the dead small animals and, feeding on the decomposed remains, contribute to the purification of the soil from the corpses, the accumulation of humus in it. Dung beetles, scarabs perform the function of orderlies, digging manure into the soil.
A huge number of flowering plants (about 90%) are pollinated by insects ( butterflies, hymenoptera). Such plants have bright flowers, aroma, nectar to attract insects. Soil insects and their larvae feed on dead plant parts, dig minks in the soil, thereby loosening the ground, and accelerate the formation of humus. A separate group consists of insects, whose representatives lay eggs in the larvae and pupae of harmful insects. it riders. The rider thrusts his egg-deposit into the body of the caterpillar, laying a huge number of eggs. Larvae emerge from them, which feed on the host's tissues and lead to its death. Developing in pests, riders reduce the number of harmful insects.
Insects, due to their diversity and abundance, play a huge and important role in nature and human life. Public insects. Most insects are solitary. However, there are social insects. These include termites, bumblebees, wasps, ants, bees. The community of these insects is one large overgrown family. There are separate groups in the family that perform different functions: they collect writing, share it with each other, care for the larvae, guard the nest. Most of the ants living in the anthill (Fig. 104) are wingless working individuals — these are barren females. The number of them sometimes reaches a million. In addition to them in the anthill lives the queen. She also has no wings. She breaks them off after the mating flight. All her life she lays eggs, and all the care of the anthill lies on the working ants. They get food, repair and clean the anthill, feed the larvae and the queen, defend the anthill in case of enemy attack. Once a year, at the beginning of summer, winged females and males appear in an anthill of pupae, which go on a mating flight. After mating, the males die, and the females shed their wings and set up a new anthill. Most ants are predators. Some feed on sweet aphids. For this, the ants protect, “graze” these insects feeding on plants, sometimes build shelters for them. Fig. 104. Cross section of an anthill: 1 - chambers with eggs; 2 - cameras with larvae: 3 - cameras with pupae Other types of ants are bred in underground chambers for feeding mushrooms, bringing crushed plant leaves there. There are herbivorous ants. Ants communicate by touching each other with antennae, legs and head. In addition, they have a "chemical language" - they emit special substances that mark their paths. By the smell of ants recognize relatives and enemies. The honeybee is a common insect. A large family of bees numbers up to 100 thousand individuals that live in a hive (Fig. 105, A). In the hive, most insects are worker bees. These are infertile females in whom the modified egg-deposit serves as a sting. They clean the hive, collect nectar, care for the uterus and the larvae, protect the hive from enemies. They live only one season (about a year). In the bee colony, the main bee is the queen, which lays eggs - up to 2000 per day. She lives about five years. In the spring, in May - June, a new queen emerges in the bee colony from the pupae, and several dozen males who are called drones: they do not take part in the work, and their main task is fertilization of the queen. An old female with a part of the worker bees leaves the hive - swarming takes place. Beekeepers collect a swarm and settle it in a new hive. In the fall, worker bees drive the remaining drones out of the hive, and they die.
Fig. 105. Bees: A - bee hive; B - the scheme of "dance" bees All concern for the hive lies with the worker bees: growing up, each worker bee changes several “professions”. First, they build honeycombs, clean the cells, feed the larvae, take food from the arriving bees and distribute it in the hive, ventilate the hive, protect it, and finally begin to fly out of the hive for nectar. Bees communicate with each other, like ants, with the help of touches and secreted substances. However, only bees have a “language of dance”. With the help of special gestures and movements, one bee can tell the others where the flowering plants are rich in nectar (Fig. 105, B). Scout bee "dancing" in the hive on the comb. The complex behavior of social insects is called instinctive, because instinct is a set of innate forms of behavior, fixed hereditarily and peculiar to a certain species of animals. The behavior of social insects is so complex that it makes many people think that it is reasonable. However, these actions of animals are instinctive, unconscious. The honeybee has long been bred by man. It is spread around the globe. A person receives beeswax, honey, various medications (propolis, bee venom, bee milk) from bees. On the underside of the abdomen of a working bee there are special glands that secrete wax. Bees build honeycombs from it. On the hind legs of bees there are areas surrounded by long chitinous hairs - baskets. Bees crawl through the flowers, and pollen falls on the hairs of their bodies. Then the bee cleans the pollen into the basket with special brushes on the legs. Soon there is formed a lump of pollen - pollen, which the bee carries into the hive. Perga - honey-soaked pollen - serves as a reserve of protein feed of the bee family. Working bees have a peculiar expansion of the esophagus - honey goiter. Collected from the flowers of nectar, which passed through the honey goiter, formed the main food stock of the bee family - honey. Honey filled cells, which the bees cover with a thin wax layer. For the year from one bee colony you can get up to 100 kg of honey. Although man has long been breeding bees, folding frame hives were invented relatively recently - in 1814. Russian beekeeper P.I. Prokopovich. Before that, in order to extract honey from a bee's nest, which, as a rule, was located in a hollowed-out deck of wood, it was necessary to break the honeycomb, that is, to destroy the bee family. A surviving swarm of bees can live on its own, without human assistance. This indicates that the bees are not yet fully domesticated. Silkworm. There are other useful insects for humans. These are silkworms. This is the only insect not found in nature in the wild state (Fig. 106). Its females even “have forgotten how to fly”. An adult insect is a thick butterfly with whitish wings up to 6 cm wide. The caterpillars of this silkworm eat only leaves of mulberry or mulberry tree.
Fig. 106. Stages of development of the silkworm: 1 - the female laying off grenade; 2 - caterpillar; 3 - cocoon formation; 5 - pupae in cocoon Scientists suggest that in the wild state the ancestor of the silkworm lived in the foothills of the Himalayas. Breed silkworm began in China about 3000 years BC. er In our time, this insect is completely domesticated. Now it is bred in China, Japan, Indochina, in Southern Europe, South America, Central Asia and the Caucasus, where the mulberry grows. There are several dozen silkworm breeds that differ in length, strength, and color of the silk thread they produce. Silkworm females lay eggs (each up to 600 eggs), which are called grenoy. From them caterpillars appear. These caterpillars are kept in special premises on the feeding shelves, fed by mulberry leaves. During pupation, each caterpillar for three days twists a cocoon of a very thin thread, the length of which reaches 1500 m. The silk thread is secreted by a special silk-gland located on the lower lip of the caterpillar. Ready silkworm silkworms are collected, treated with hot steam, and then silk machines are unwound with special machines. Part of the cocoons is left for breeding butterflies for reproduction. Silk is used in light industry for the production of fabrics, in medicine (yarns are made from it for stitching wounds) and in aviation. Insect protection. A person greatly influences the environment (plows open virgin steppes, cuts down forests, uses toxic chemicals). Therefore, the number of many species of animals, including insects, is declining. Some species are on the verge of extinction. In this regard, rare species of insects are taken under oxpairy. The Red Books were created, containing information on specially protected rare animals (Fig. 107), the reasons for their distress and measures of protection. Among the insects of our country listed in the Red Book, there is a steppe dyke - a large steppe grasshopper that lives in the steppes in southern Russia. The area of distribution of this grasshopper was reduced in connection with the plowing of virgin steppes. From the beetles, several species of large predatory beetles, ground beetles, fell on the pages of the Red Book. In the south of the Far East, the largest beetle of Russia is protected - relic woodcutter, whose body length reaches 10.8 cm, larvae up to 17 cm.
Fig. 107. Rare and protected insects: 1 - steppe dyke; 2 - Apollo; 3 - Far Eastern relic woodcutter; 4 - Caucasian ground beetle; 5 - wall bumblebee; 6 - Zenobia pearl Many species of bumblebees are listed in the Red Book, for example, the bumblebee is changeable and the steppe bumblebee. Among the butterflies listed in the Red Book, can be called Apollop, mpemozina, pearl zenobia. They are protected by the Law on the Protection of the Animal World. The role of insects in natural communities is enormous. Insects are the most important pollinators of flowering plants. They serve as food for various invertebrates (spiders, millipedes), fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and beasts, even some insectivorous plants (sundew). Among insects there are a lot of orderlies who help to process organic remains of plants and animals into mineral substances. Soil insects and their larvae increase the fertility of the soil, mixing and fertilizing it with their excrement. The role of insects in the cycle of substances in nature. Exercises on the material
A lesson on the topic "Bees and ants public-insects" Purpose: - highlight the structural features of the honeybee and ant in connection with the social way of life; Show the role in nature and importance in human life; prove the need to protect these insects; - broaden the minds of students. Teaching methods : reproductive, exploratory, research, method of collective decision making Type of lesson: learning new material. Class form : educational project. Project typology : informational - research, short-term. Equipment: multimedia projector, presentation “Bees and ants — public insects, books, handouts, didactic cards. Classroom organization form : classroom, group, individual. Lesson content: I . Organizing time (Mutual greeting of students and teachers, fixing absentees, checking students' readiness for a lesson) Stage call: Before telling the topic of today's lesson, I will make riddles for you, and you have to guess what will be discussed in the lesson. 1. I smell summer and pollen. I fly to the flowers by a bullet. But I am very angry. To the one who climbs into the hive! 2. In a clearing near Christmas trees The house is built of needles. Over the grass is not visible, And there are a million tenants in it. II . Preparation for the main stage of learning material mastering. . Activation of supporting knowledge and skills. - In previous lessons we began to study the most numerous type of animals - the type of Arthropods.What signs of this type are observed in bees and ant? (I listen to the answers of the children). Articulate limbs The presence of chitinous cover. To which class would you assign these animals to? (to the class of insects). As you already understood, the heroes of our lesson will bebees and ants. In view of the fact that there is a lot of information about these insects, we will study this topic as part of the project. Project goals: Examine the systematic position of the honeybee and ant; study the structure of the honeybee; study polymorphism in the hive and anthill; find signs of similarities and differences; to study the meaning of bees and ants in nature and human life; insect protection; study the history of beekeeping; to conclude why bees and ants are classified as public animals; present our project. III Stages of work on the project. 1. 3 groups of students are being formed: Each group receives an instructional map, which contains a plan for studying the topic area. Sheets- answer. In today's lesson, work will be done in groups "Theorists", 2 "Beekeepers", 3 "Biologists". The request to the group members to remember the rules of work in the group, to respect the time. 20 minutes are given for group work, the speaker’s speech time is 3-4 minutes. Please start by reading the instruction card. I wish you good luck. Instructive card "THEORETICS" Purpose: to study the systematic position of the honeybee and ant, find out their importance in nature and human life, suggest measures for the protection of insects. 1. The systematic position of the bee and ant. 2. External structure of a bee: Consider in more detail the structure of the working bees in Fig. 1 (reference material) and answer the questions? Which parts of the bee's body is divided? How many pairs of wings? How many pairs of legs? What senses are different on a bee's head? Features in the structure of the hind legs. What do you think, what are they for? 3. What is the value of bees and ants in nature and human life. 4. Offer measures for the protection of insects. 5. Make a conclusion why bees and ants are called social insects? Beekeepers instruction card Purpose: study the history of beekeeping. 1. How could we find out that a bee has become a man's pet since time immemorial? 3. What kind of bee products paid tribute, taxes and taxes? 4. What did the ancient Slavs use instead of sugar, and what for light? 5. What was the name of the ancient beekeeping? 6. What did the Ukrainian landowner Peter Ivanovich Prokopovich invented in 1814? 7. Draw a conclusion that reflects the value of bees in nature and human life. Instructional card "Biologists" Purpose: study polymorphism in the hive and anthill; find signs of similarities and differences. Theoretical part. 1. Polymorphism of a bee family. 2. The polymorphism of the ant family. 3. What is called swarming? What is its biological role? The practical part. Using the material of the textbook pages 135-136 and reference material fill in the table"Polymorphism of bees and ants" Signs of comparison. Polymorphism of bees and ants Uterus bees Uterus ants Drone Male ant Working bee Working ants 1. Body size. l = 18-20 mm m = 0.25 g Up to 50 mm l = 15-16 mm m = 0.2 g Up to 50 mm l = 12-14 mm m = 0.1 g 2 mm 2. The number of individuals in the family. 1 2 or more Some tens From several dozen to several hundred 70 000 From a few tens to a million 3. Terms of life. Up to 5 years 12-20 years 1 season Few days weeks 1 season Up to 3 years 4. Features of the structure. Big bee, long pointed abdomen; associated with its reproductive function similar to the workers, but differ from them in the structure of the breast and larger size. Have wings that bite themselves after fertilization. medium-sized bee with very large eyes in contact at the back of the head,belly round Develop from unfertilized eggs, have wings on hind legsbaskets , on the abdomen of the mirror, the expansion of the esophagus - honey swell; at the end of the abdomensting Females with underdeveloped reproductive system , They have no wings, there is a simplified breast structure, the eyes are smaller than those of females, or absent 5. Functions performed. Pairing and laying eggs Pairing And laying eggs Fertilization females Female fertilization Cell cleaning, feeding the uterus and larvae, building honeycombs, prospecting, collecting food, protecting the hive. Family care (Guards, "nannies", clean the nest, etc.) Answer the questions? 1. Give the concept of polymorphism? 2. Make a conclusion of what is polymorphism in bees and ants, with what it is connected. 2. Search for information. Students are asked to find answers to the questions indicated in the instruction card. Students work with a textbook, additional literature. 3. Processing Information . Students in groups fill out response cards, prepare a presentation - the protection of the project, determine the speaker from their group. 4. Protecting the project. Representatives of each group present their work, talk about their achievements, draw conclusions: 1. The bee and the products of its vital activity are of great practical importance. But the greatest importance of the activity of bees is manifested in pollination of plants. 2. The bee colony consists of the queen, the drones, and the worker bees. Between them in the family responsibilities. 4. Features of the structure of the working bees associated with its "professional" responsibilities. 5. The bee and the ant are a “social” insect with complex instinctive behavior, in their caring care for the “baby”, in the expediency of the division of labor between family members, in their amazing construction art IV . Homework. Tasks to choose from: Prepare reports on the silkworm Silk production Insects listed in the Red Book. V . Results of the lesson and reflection. You guys did a great job. I make a comment. And I propose to briefly answer the questions What is your mood? Please continue the phrase It was interesting to me… We figured out today ... I realized today that ... It was hard for me ... Tomorrow I want a lesson ... show all Peculiarities of behavior of social insectsThe behavior of insects is determined by the combination of conditioned and unconditioned reflexes, instincts, taxis and tropism (for more details, read about this). In social insects living in colonies and difficult to interact with each other, all these components of behavior are present, but their instincts are the most pronounced - long chains of reflexes, launched one after another by a kind of “domino effect”. Sometimes instinctive behavior leads to such complex sets of actions that it is difficult to believe that ants, termites, bees, and os lack the ability to think and fully communicate with each other. For the manifestation of instincts and other complex forms of behavior are responsible specific areas of the brain. For many social insects, these areas are very well developed and are larger in size than others. For example, the so-called mushroom bodies responsible for the integration of information received from the sense organs occupy one sixth of the brain volume of a honey bee, and one third of the Formica ant. The brain itself is also developed more strongly in comparison with other insects. Key features of the behavior of social insects are as follows: This can be illustrated by the example of another experience. A special device was installed near the road of a small forest ant: two cameras, two curtains covering each of these cameras, and two threads connected to the curtains. If the ant was pulling with one thread, the curtain opened, and the insect received sugar syrup as a reward. There was nothing behind the other curtain. The ants quickly realized what was happening, and opened the chamber in which the syrup was located, more than 60 times per hour. Moreover, sometimes some ants pulled the thread, keeping the curtain open and yielding to others the right to feast on syrup. Another feature is that social insects purposefully and smoothly can perform one common work, necessary for the sake of the interests of the colony. They build anthills, get food, carry out laying and care for them in accordance with some tacit agreement, in which each member of the community has a certain role. (a photo) Caste Behavior and SeparationIt would be impossible to ensure the autonomous existence of a colony if all insects in the group had “equal rights”. Therefore, within the family, social insects are usually divided into castes - subgroups, whose representatives perform certain tasks. Using the bees as an example, one can see that in the hive there is one single womb that lays several drones that fertilize it, and all other individuals are worker bees. They are responsible for life support, storing food, caring for eggs and etc. Accordingly, these three subgroups have completely different behaviors. Even more difficult device community in ants. In some genera and species of ants, “scouts”, “foragers”, “warriors”, “aquifers”, “nurses”, etc. are distinguished from working individuals. In total, one anthill can number up to 11 castes, and they behave, respectively, in different ways. The behavior of social insects in general is very complex. But within each family, the “deeds” of its individual members are more similar than the actions of different insects of the same species, leading a solitary lifestyle. This is explained by the fact that in the group insects live in approximately the same conditions, so they develop similar conditioned reflexes and form similar life experiences. However, each insect of a family is unique. It has been found that learning ability and other innate properties vary among different community members, even within the same caste. In other words, as among people, among ants, bees, etc. there are "stupid" and "smart." Their behavior is different. WaspsThere are many more examples of how surprising behavior of social insects can be. But even these examples make us convinced that in their development the representatives of the class Insecta sometimes even surpass the organisms that are at a higher level of evolution. It is precisely the behaviors of social insects that still force some specialists to express the opinion that, probably, along with everything else (reflexes, instincts, etc.), insects have rudimentary forms of rational activity. |
Popular:
New
- Markup definition. Planar marking. Types of markup. Questions for self-test
- Pipe bending machines Various variations of pipe bending machine
- Safety during filing
- What should be the sharpening angle of the scriber
- Drawing on preparation of contours of future product
- Modern ways of cutting metal and its defects
- Kerner - so that the drill does not slip off!
- Objects of inanimate nature Examples of the influence of inanimate nature factors on plants
- Finishing joinery
- Block breakdown in AutoCAD - simple and effective teams from practitioners