Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Artificial flowers and their secret
- Completion of country houses
- Design project of a three-room apartment
- Is it possible to build a balcony on the second floor
- Overview of the room interior with a balcony
- Kill neighbors that interfere with sleep
- Sample collective complaint against neighbors
- How to teach lesson to noisy neighbors
- We put things in order in kitchen cabinets and drawers
- Interesting interior solutions for different rooms
Advertising
| We make natural ventilation in the country house with our own hands. Do I need artificial ventilation in a country house or cottage |
|
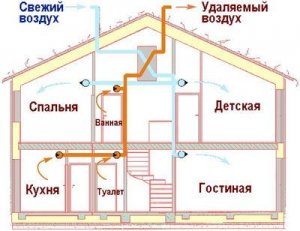
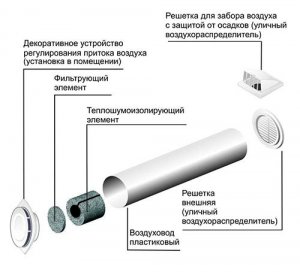
How nowadays do ventilation in country houses? A hole was made to the street from the bathroom, the fan was installed and ready. Carbon dioxide? Humidity? No, not heard. Therefore, a headache, a breakdown, condensation on the windows, mold and other delights of the lack of fresh air from the street. Let's figure out how to properly make ventilation in a country house to avoid mold and maintain their health. Let's get started! 3. About few ventilation people think about. A fan was installed in the bathroom and enough. And then the surprise begins, why the gas stove, fireplace do not burn well, condensation falls out on the windows, and you see the mold. All this is a consequence of the fact that the concentration of carbon dioxide begins to increase inside the house and the humidity rises (a person exhales steam). But the biggest joke in another. Suppose you set a fan to blow out of the bathroom. Turned it on. He begins to draw air from the house. And where will the new air in the house come from? Here, look at the video with what effort the front door to the house opens if you leave all the windows closed: The conclusion is simple - in any home, an influx of fresh air is absolutely necessary. In old houses, the air flow was through the leaks of the walling and, in particular, through leaking window frames. Now everyone puts “warm” plastic double-glazed windows, and they are completely tight. In principle, in the warm season, you can always keep the windows open, and this is more than enough for full air exchange inside the house. But problems begin in the cold season. After all, the windows are closed so that it is not cold! 4. As you recall, my house is heated by an air heat pump, in other words, a channel air conditioner, which is effective at temperatures up to -20 degrees Celsius. This type of heating provides a minimum of 2.5-fold energy savings for heating. Below is a diagram of the supply ducts laid under the ceiling. Through them hot air is supplied to all rooms. Return air is taken from the floor in the lobby. But this is recycled air! To ensure the flow of fresh air, a separate 125 mm channel is connected to the intake duct from the street (indicated in green in the diagram), and exhaust air is discharged through the channel in the bathroom (an exhaust hood from the kitchen is connected to it - indicated in gray). Such a scheme is functional only in the warm season. As soon as freezing occurs on the supply air duct, icy street air will be sucked into the house. This will create an additional load on the heat pump, which will be difficult to warm the icy street air mixed with warm from the room. Therefore, it is necessary to install a channel heater with a special controller on the supply air duct. The point is that the duct heater only warms the fresh street air necessary to ensure the comfort of people in the house. And the air heat pump compensates for the heat loss of the building. It is more efficient to install a recuperator instead of a channel heater, but with air exchange volumes of less than 150 m3 per hour - the payback period will be more than 7-8 years. A vent window does not effectively provide the necessary fresh air flow because it is uncontrolled air exchange and therefore large heat loss. 5. So, a supply 125 mm air channel. The passage through the wall must be insulated as this is a place of a sharp temperature drop and moisture will condense from the side of the room on the duct. 6. Not necessarily, but preferably a simple air filter. At least a metal mesh, so that in no case insects do not get on the heating element. Left filter after 40 days of operation. Environmentally friendly area, lack of production and all that. The filter is easily washed with water and installed back. 7. The next element is the channel heater. Inside it are two spiral heating elements with a total power of 2 kW. 8. And the "heart" of the system is the triac power regulator TC-3.7 / 1. This device, based on the readings of an external temperature sensor, makes it possible to maintain a predetermined temperature with high accuracy by applying a partial or full load to the heating element. 9. After the channel heater, a temperature sensor is installed in the duct. 10. You must have seen similar devices in hotels and multi-story buildings with centralized air heating. Each room has a separate controller that heats the air to the set temperature. Why it is impossible to control the load with a conventional temperature controller? It's simple, we have a heating element with a power of 2 kW, imagine what kind of surges will be in the electric network each time it is turned on / off. Total, the internal block of the air heat pump works for me round-the-clock both in the winter and in the summer. The fan in the bathroom at a low speed, providing an air flow of 90 m3 / hour, also works around the clock. I set the street air heating to a temperature of +10 +15 degrees Celsius, the rest heats up the heat pump. Focusing on the statistics of last winter, we can say the following. In the coldest winter month, I consumed 300 kWh of electricity to heat the supply air in the amount of 90 m3 / h. And to compensate for the heat loss of the building, it took 600 kWh of thermal power. Budget supply ventilation (at prices in autumn 2014): duct heater - 2500 rubles, seven-core controller - 5000 rubles, temperature sensor - 1000 rubles, air ducts and connecting elements - 1000 rubles. A more economical alternative is a recuperator, but its cost at that time was at least 60 thousand rubles, that is, 6 times more expensive. In my case, the presence of air heating made it possible not to make separate supply ducts with fresh street air into the living quarters. If you use radiators or underfloor heating, then you need to lay separate air ducts with fresh air in all living quarters (at least bedrooms). And do not forget that the combustion process also requires an influx of fresh air (not to mention the emission of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide). Bad draft by the fireplace or stove? So your house is airtight, there is no influx of fresh air! 12. And a bonus photo of the guest house. It remains to close the base and finish a couple of little things. By the way, it is also heated by an air heat pump - a window air conditioner, which I bought for 7 thousand rubles. Separately, I’ll also tell about summer kitchen. The article will be considered types of ventilation systems, their pluses and minuses, of what structural elements the ventilation system consists of, and also you will learn how to mount the system supply and exhaust ventilation. As you know, fresh clean air, saturated with oxygen, has a beneficial effect on human health, and a well-designed and installed ventilation system will ensure a comfortable stay indoors. According to SNiP 2.08.01-89 * Appendix 4, the amount of air removed is: For living rooms - 3 m 3 / h for 1 m 2; For kitchen: With a 2-comfortable stove - 60 m 3 / h; With a 3-comfortable cooker - 75 m 3 / h; With a 4-comfort cooker - 90 m 3 / h. For a bath - 25 m 3 / h; For the restroom - 25 m 3 / h; For the combined premises of the restroom and bathroom - 50 m 3 / h; Accordingly, the volume of incoming outdoor air should be equal to the volume of air removed from the room. For living rooms (living rooms, bedrooms), the influx of fresh air should be at least 30 m 3 / h per person. Types of ventilation systemsThere are two types of ventilation systems: natural ventilation and forced ventilation. Natural ventilation premises is due to the temperature difference between the external and internal air. As you know, the density of cold air is greater than the density of heated air. Due to this, cold air descends, displacing warm air. So there is a pressure difference between the external and internal air. Due to this pressure difference, the outside cold air tends to a low pressure zone, i.e. into the room with warm air, and warm air is forced out of the room and rises out through the ventilation duct. Thereby, a draft occurs in the ventilation duct. The natural ventilation system works by this principle. The benefits of natural ventilation : Cheap to install and operate; Easy installation; It does not break; It is independent of electricity. Cons of natural ventilation : It has limited performance adjustment, it is adjustable only in the direction of lowering productivity; Large heat loss during natural ventilation in winter; Natural ventilation cannot work in the summer because the air temperature inside and outside is almost the same; No air filtration. Forced ventilation It works thanks to the creation of artificial fresh air and artificial draft in the exhaust duct by the fans. This system allows you to fully control the air exchange in the room. But the performance of forced ventilation is completely dependent on the availability of electricity in the house. If for some reason there is no electricity in the house, then forced ventilation will immediately stop its work. Therefore, such ventilation requires a backup power supply in the house. Benefits of fresh air ventilation : Performance adjustment, both upward and downward; The efficiency of the supply ventilation does not depend on the outside temperature; Possibility of filtering, heating, cooling, humidification and dehumidification of air; Minimal heat loss due to heating of cold outdoor air. Cons of supply ventilation : Supply ventilation does not work if there is no electricity in the house; Additional energy costs, periodic replacement of filters; Elements of forced ventilation can fail; Requires sound insulation, as makes some noise. Considering all the above-mentioned pros and cons of natural and forced ventilation, as well as the costs of materials and installation of ventilation, choose the most suitable type of ventilation for yourself. Elements of the ventilation system Natural ventilation system consists of the minimum required structural elements: supply valvethrough which fresh air enters the room (an open window may act as an alternative to the supply valve) and exhaust pipethrough which the exhaust air is discharged to the outside. A deflector is installed above the chimney.
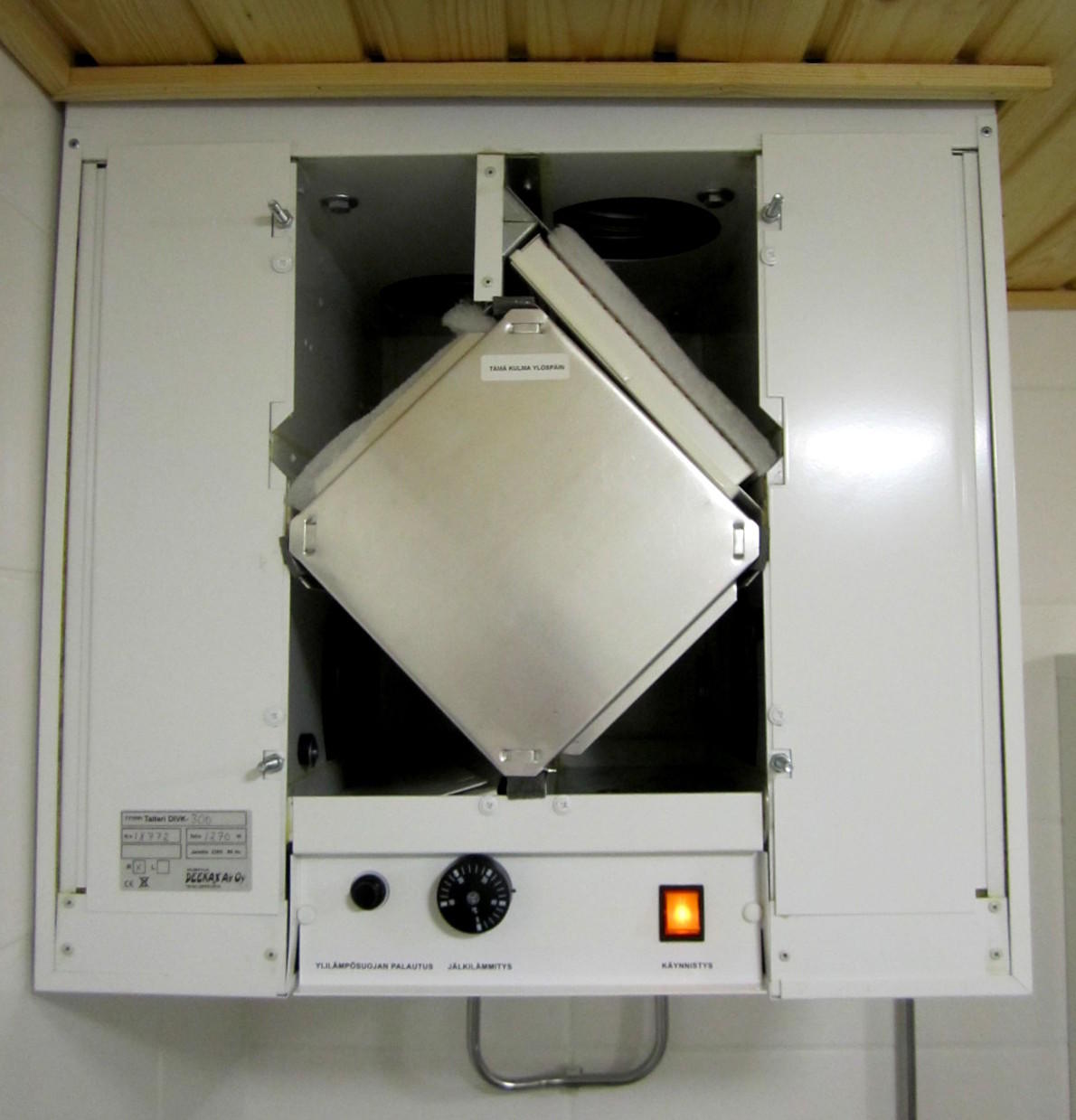
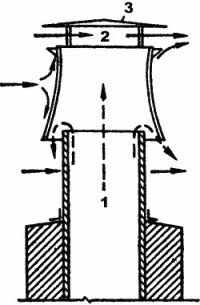
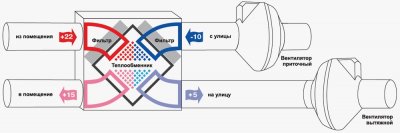
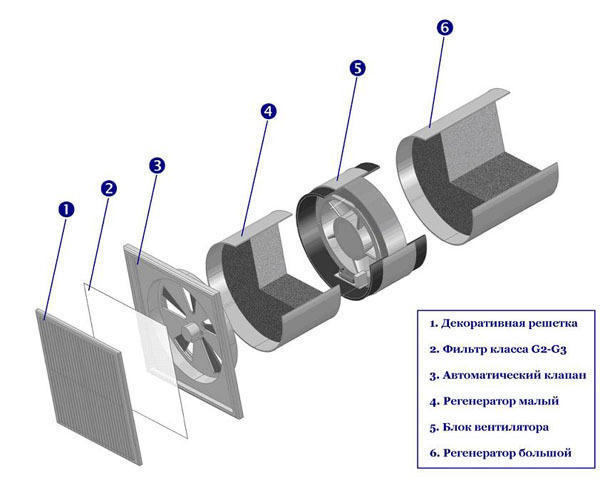
- this is a device that increases draft in the ventilation pipe, creating a low pressure zone around itself due to design features, thereby sucking air from the exhaust pipe. That's all the elements that make up natural ventilation. Forced ventilation consists of a lot more components. The entire forced ventilation system is centered around one important element - supply and exhaust unit. This unit provides both fresh air intake and exhaust air removal. Consists of the following elements: supply fan, exhaust fan, recuperator, air heater, bypass and filters. Let's take a closer look at how these seemingly complex elements work. WITH supply and exhaust fan everything is clear, one pumps air into the room, and the other takes the "dirty" air out. Supply air filter prevents dust, insects, plant pollen, etc. from getting into the house and into the ventilation system itself. Extract air filter protects the supply and exhaust unit from the ingress of house dust, thereby increasing its service life. After fans and filters, air enters the recuperator.
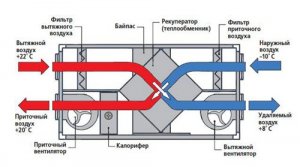
Recuperator or the heat exchanger heats the incoming cold air due to the warm exhaust air, while the incoming and outgoing air flows are not mixed. This is achieved due to the close arrangement of the supply and exhaust channels. Thanks to the recuperator, the heat loss at home is significantly reduced. As you know, with the close interaction of air flows with positive and negative temperatures, condensate forms. And this condensate is formed, of course, in the recuperator. At fairly low outdoor temperatures, this condensate freezes, forming ice in the channels of the heat exchanger. This ice can clog and damage the channels. To prevent this from happening, we added to the block bypass, which allows you to direct cold air bypassing the recuperator. Thanks to the bypass, the recuperator is heated by the warm exhaust air, the ice formed in it melts. Even when passing through the recuperator, the cold air does not heat up enough to ensure a comfortable stay in the house. Therefore, after the recuperator there is a heating element called air heaterwhich heats fresh air to a comfortable temperature. Some expensive block models have built-in humidifiers, to moisten dry winter air. The supply and exhaust unit has a control and automatic control system, which allows you to set certain values \u200b\u200bof air temperature, air flow rate, degree of air humidification. It is desirable to place the supply and exhaust unit in the attic of the house so that the length of the ducts is minimal. Air ducts cross-section differ into round and rectangular. Round ducts have less resistance when air flows through them, which in turn reduces pressure losses in the system and reduces noise.
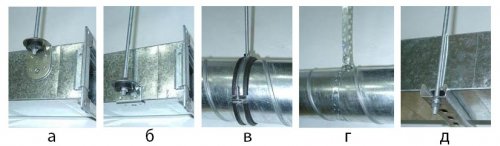
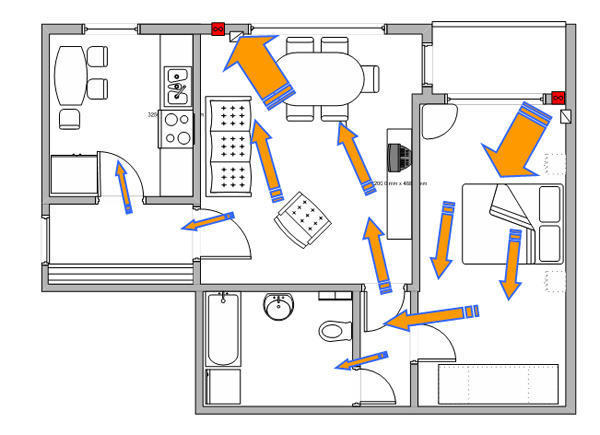
Rectangular ducts have more resistance than round ones, but they take up less space and their use is justified when the space for ventilation is limited. Also, air ducts vary in material and are metal, plastic, metal-plastic, foil and textile. When choosing air ducts, consider the environment in which they will be used: temperature and humidity. Consult a specialist to determine duct sizes. At installation of air ducts various shaped products: tees, crosses, bends for changing the direction of the duct, adapters from one diameter of the duct to another, adapters from round to rectangular, plugs, nipples for connecting ducts, etc. And finally, at the outlet of the supply air duct anemostat - a device that evenly distributes throughout the room the air flow coming from the duct. Installation of supply and exhaust ventilation systemThe design of the ventilation system should begin at the design stage of the house, as air ducts suspended from the ceiling and closed by tension or false ceilings will be subtracted from the total height of the room 15-20 cm. When arranging the ducts inside the wall frame, the wall thickness should be taken into account at the design stage of the house. Air inlet and the deflector must be placed at a distance of at least 10 meters, ideally the air intake hole is on one side of the house, and the deflector on the other. The air intake hole is placed at a height of not less than 1.5 m, so as not to trap the radioactive soil gas radon in the ventilation system, which negatively affects human health. The inlet ventilation hole itself is covered with a net to avoid leaves, insects, birds, etc. getting into the ventilation system. Air outlets placed in places of high air pollution: kitchen, bathroom, toilet. In the kitchen, an influx of fresh air is not needed, only an extractor fan. Each living room must have a separate supply air duct. For each of the premises, a separate duct should be maintained for exhaust air, i.e. air outlets from different rooms should be connected with air ducts in parallel, and not in series, then the smell from the toilet will not appear in the kitchen, and the smell from the kitchen and toilet will not be in the bedroom. Thus, all air outlets should be connected directly in front of the exhaust outlet of the supply and exhaust unit. Hard ducts should not be connected directly to the ventilation unit, otherwise vibration and noise from the unit will be transmitted through the ducts to the room. Therefore, you must connect the rigid ducts and the unit only through flexible corrugated ducts and the length of the flexible section must be at least 1 m. All ducts are glued with a layer thermal insulation 10-15 mm thick. This will prevent moisture condensation in the duct and prevent the transmission of noise and vibration through the ducts. Try to position the ducts with the smallest angle of rotation, as air ducts located at right angles sharply reduce the pressure in the system and thereby reduce the efficiency of the ventilation system. In addition, the pressure in the system decreases with increasing length of the ducts, so the length of the duct should be minimal. Fixing circular ducts carried out using a clamp with a hairpin (c), or using a punched tape (g). Rectangular ducts produced usingZ -shaped (b) orL -shaped profile (a) and studs, or with the help of a traverse and studs (e). Supply and exhaust ventilation unit it is advisable to place in the center of the house in the attic, so that the ducts have a minimum length. It is also necessary to provide free access to the ventilation unit, as filters are periodically changed and maintenance block. That's all you need to know at the initial design stage. ventilation systems in a private house. Subscribe to new articles in which you will find even more useful and detailed information about country house ventilation systems. Want to receive new articles in the mail? A country house is an island of comfort and prosperity. For the house to become so, it is necessary to provide in it everything necessary for life. Ventilation country house is far from last in importance. It provides a favorable microclimate, maintains a healthy atmosphere. The ventilation system in country houses is designed at the stage of designing the entire house, as a separate section. Usually, only natural ventilation is provided. After putting the housing into operation, it may be necessary to change the ventilation system in the country house. Our experts are ready to come to your aid in arranging the ventilation system. VentStroyProm - extensive experience in creating ventilation systems The VentStroyProm company renders services in design, installation of air exchange systems at any objects. We work in the field of housing. We make projects and install the ventilation of a country house, cottage, pools and saunas. The specifics of the design and installation of ventilation of a country house The ventilation system in a country house is individually designed. The project must take into account the area of \u200b\u200bthe building, the set of premises and their purpose. Does the house have a pool, sauna? Then it is necessary to equip a ventilation system that can remove excess moisture from the room. In rooms equipped with a fireplace, they create such a balance of exhaust and air flow that combustion is maintained at the desired level. In the boiler room, the project usually provides for autonomous ventilation. Its task: the removal of combustion products and ensuring the optimal level of operation of the boiler, in order to prevent excessive consumption of fuel. The ventilation system in a country house provides for the installation of ventilation in the attached garage, workshop. From these rooms, air is removed and not allowed in residential premises. Favorable conditions for customers
Free expert visit to the facility
Selection of the best equipment option
Warranty for work and equipment up to 3 years
Preparation of a commercial proposal in 1 day
Start of work without advance payment
Service support during operationWe carry out work for legal entities and individuals Prices for installation of ventilation Typical ventilation solutions. ECONOMYDomestic equipment Working draft Reliability Compliance Shortest terms of work STANDARDDomestic and world equipment Standard projects Silent system Compactness Optimum energy efficiency PremiumWorld brands Individual project Silent system Energy efficiency Individual climate control Which ventilation system to prefer? For suburban housing the best way - supply and exhaust ventilation. Its advantages:
Specialists always give a guarantee for their work, perform it the first time, qualitatively and without errors. 0years in business 0of customers 0seconds on this site Essence supply and exhaust system ventilation The design of the air exchange system provides for the installation of supply and exhaust fans, air ducts and deflectors. The design and installation of the system is carried out taking into account the location of the premises, their purpose. An exhaust fan is often installed on the roof of a home. So it does not bother anyone, does not violate the aesthetic appearance of the house, and works with maximum efficiency. The supply air in the country house is additionally heated in the winter and air-conditioned in the summer. It is optimal to install filters for air purification on the supply fans. Typically, a draft ventilation system in suburban housing is prepared before construction. But if you need to upgrade or change the ventilation system, then this is easy to do. Installation of ventilation installations, air ducts in a suburban housing is carried out in a short time, minimally affecting the existing finish. The supply unit is mounted in the utility rooms. What does VentStroyProm offer:
We guarantee a pleasant atmosphere in the house! You may be interested × Close The composition of the supply and exhaust unit "ECONOM" class Stitched type-setting unit consisting of: Type-type exhaust installation consisting of: Control module for supply and exhaust installation, consisting of: Order pricing × Close The composition of the supply and exhaust unit "STANDARD" class 1. Inflow unit monoblock type consisting of: Monoblock type exhaust unit consisting of: Forced-air and exhaust installation of monoblock type Module No. 1 consisting of: Module No. 2 consisting of: Control module for supply and exhaust monoblock installation consisting of: Order pricing Nowadays, few people build traditional huts with stoves, preferring modern engineering and architectural solutions. As a diverse and inexhaustible post shows, ventilation problems in the minds of the ordinary owner of a country house occupy, at best, 47th place (I hope this statement will not offend anyone). And psychologically, this is easily explained: if a city dweller broke out of the metropolis and found himself in nature, then by something, and he would be provided with fresh air by definition.
However flavors and mowed hay won't get into an unventilated house, and that's why:
How much air do we need?Imagine these volumes of air, expressed in numbers, are well known and fixed in the relevant building codes. According to the SNIP, for living rooms (at the time of the presence of residents there) it is necessary not less than a single exchange of air volume for 1 hour. That is, if you live in a bedroom of 16 square meters. m and a ceiling height of 3 m, then an hour for a quiet sleep, the owners will need 50 cubic meters of air. By the way, its weight is 60 kg. During the night in this bedroom it should be replaced to half a ton. Rate this figure. Where is the car that “drives” 400 cubic meters of air through the room?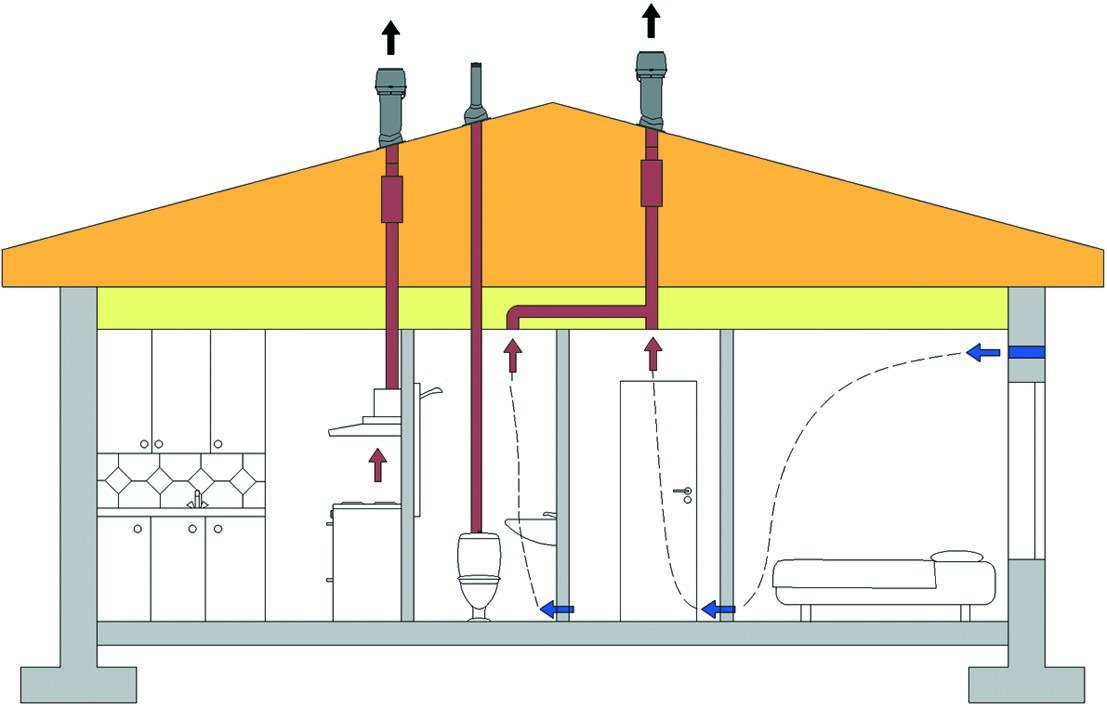 The situation in common areas is noticeably more serious. SNIP determines that:
Available on some window models special valves for ventilation they don’t solve the problem radically: the best of them are able to let in no more than 20 cubes of air per hour. Those who studied the previous paragraph, this “twenty” is unlikely to be seductive. Two versions of climate comfortKnown 2 ventilation systems: with natural and forced air exchange. The main disadvantage of the first is that its effectiveness depends on variable factors: air temperature, wind direction and speed. In order for the draft to work energetically, the outdoor temperature should be about 0 ° C or lower, and the minimum difference between the level of indoor air intake (i.e. the height of the intake grilles or at least the ventilation window) and its discharge (the height of the head or ventilation duct) - not less than 3 meters.
For a one-story cottage, this is not at all characteristic. As soon as the street gets warmer, and such a system generally stops working. I recall the sizzling summer of 2010, which I spent in a one-story frame house with a fairly high ventilation pipe. The result of natural ventilation in the heat is zero. You bring a piece of paper to the edge of the channel, but it will not move. Those. hopes for natural ventilation, just when it is desperately needed, have completely vanished. Therefore, in order to provide climatic comfort at the cottage, it is equipped forced mechanical ventilation systemsindependent of the temperature fluctuations of the outdoor air and the height of the ventilation pipe.
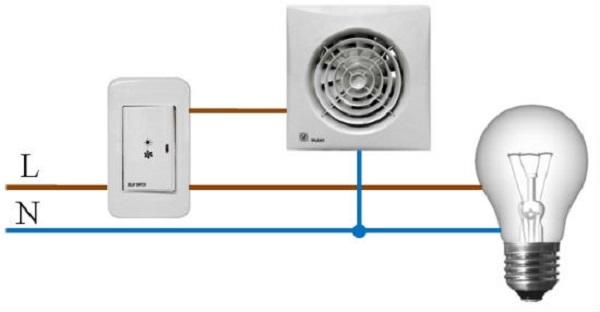
Mechanical ventilation is especially needed in rooms that are problematic in temperature, humidity and odors: boiler rooms, built-in garages, laundry rooms, workshops. Removing stagnant air: forced ventilationThe easiest forced ventilation option includes active hood and natural flow. In it, polluted air is mechanically evacuated outside the house. For this, various kinds of paddle fans. They create a small vacuum on the edge of the ventilation duct, which draws polluted air from the premises. In his place, according to the laws of physics on the equality of pressure in communicating vessels, fresh air enters - through ajar windows (or slots in them), a gap under the door, etc. For stable operation of such ventilation it is necessary atmospheric connectivity. Doors with a sealed vestibule should be at least ajar. With the windows and doors closed, the polluted air will not leave the country house: the fans, even if they are turned on at full power, will “choke” and fail prematurely.  It is also appropriate to talk about collateral individual hoods in the toilet and bathrooms, in the kitchen, as well as in technical rooms. Installed in them local fans by design are divided into axial and centrifugal. Their work schedule depends on the purpose of the ventilated rooms. Agree, why spend a fan in the bathroom while nobody is there? Nothing at all! Therefore, such fans are equipped with different (according to the principle of operation) sensors - movement, humidity, etc. In the toilet, for example, it is reasonable to connect the fan to the switch.
However, even this seemingly simple thing has its own nuances. So, for obvious reasons, it is advisable to extend the operation of the toilet fan for 5-10 minutes after turning off the light. A simple time switch included in the electric circuit of the fan will solve this delicate problem. Wall fans remove air through the channels provided in the walls during the construction of the house. If you are building a house anew, then the possibility of optimal ventilation of the premises should already be included in the project. To do this, it’s better not to "scatter" on local ones, but install them in the back room or in the attic central exhaustfanone for the whole country. It is connected to the exhaust objects with air ducts. For central exhaust fans centrifugal circuitcapable of "shoveling" the air from several suction ducts. Such devices have a reduced noise level, and yet it is better to place them away from the bedroom and the nursery. We blow in both directions: systems of supply and exhaust ventilationIt is difficult to find flaws in the considered systems in warm weather, however, they are detected with the advent of cold weather. The fact is that air in winter goes inside without preheating. Of course, this leads to drafts and local overcooling of rooms. In winter and summer, such systems not designed to clean air from dust and odors. This set of shortcomings has led to the creation of a more perfect ventilation systems. It supplies to the premises a sufficient amount of purified and, if required by the weather, heated fresh air. A waste displays with the help of fans.
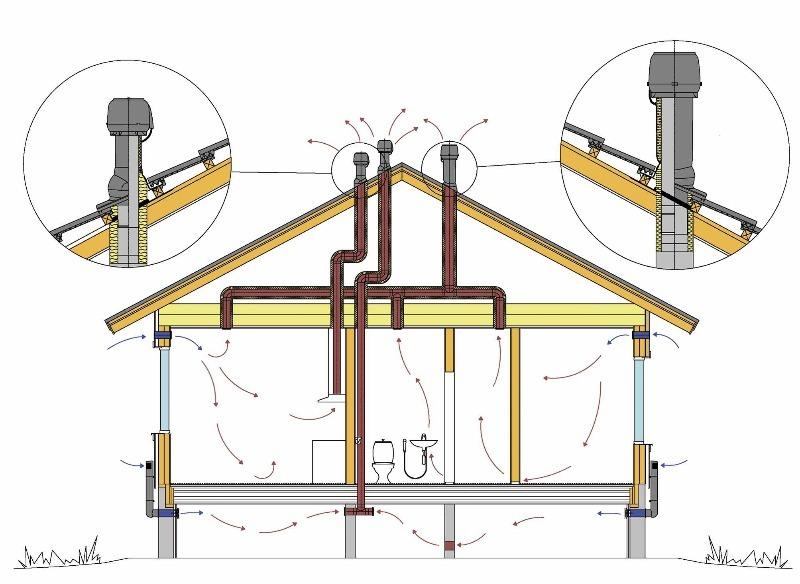
It is wise to install such ventilation systems in houses adjacent to freeways. They will not allow the car stench to poison country life. This installation is also required in rooms with a pool. But creating a comfortable microclimate in them is a big separate topic, which we will not consider today. For forced supply of fresh air, it is wise to use factory one-piece air handling units, and not engage in amateur activity. Although creative and masterful summer residents may disagree with me. For this we respect them. Installations are mounted in the attic or outside the house. After cleaning and heat treatment, air enters the rooms through a duct network. The location of the ducts should also be provided at the design stage. Most often they are placed behind a false ceiling. And this "eats" 10-15 cm of the height of the room. Often paired with a supply unit roof exhaust fan. Of course supply unit and the exhaust fan must "pull" synchronously, otherwise in the country will be either increased or decreased pressure.
We pass to serious technologies. That is, not “clumsy” distillation of air from empty to empty, but to the careful use of thermal energy accumulated in the house. This is a ventilation system based on an energy-saving supply and exhaust system with a plate heat exchanger or rotary heat exchanger. Traditionally, the installation is mounted in the attic. For air exchange, 2 duct networks are constructed:
Forced-air and exhaust installations with recuperator reduce the cost of heating the supply air by 10-70%. They are based on a plate cross-flow recuperator - a package of thin metal plates, between which there are gaps. The air removed from the room flows into every second gap between the plates, and fresh air flows through the remaining channels. Since the plates are very thin, they easily transfer heat from a heated air stream to a colder one. Forced-air and exhaust installations with rotor heat exchangers Imported production - the pinnacle of ventilation with maximum energy savings. But they are quite expensive and in ordinary dachas have not yet received distribution. However, I would like to complete the article with an encouraging story about one wonderful domestic developmentworthy embodied in metal. It was created in industrial Omsk, at the Ecoterm enterprise. The installation is called UVRK-50. To understand the essence of her work, we can draw an analogy with how we breathe in severe frost - through a warm woolen muffler. During exhalation, part of the heat and moisture is given to him, and when inhaling, fresh air, passing through matter, absorbs heat and moisture and returns them to the body. This ensures ventilation with optimal energy saving. When using this system applies joint work of two installations in neighboring rooms. They alternately automatically include a different direction of flow and provide fresh clean air to an apartment of 60 square meters. m with minimal energy loss. Power consumption does not exceed 30 W, and the noise level is 42 dB.
The inlets of the installation are lined with grilles located both in the interior and on the facade of the cottage. An unsatisfactory, I would say ugly, state of air in rooms with closed double-glazed windows prompted the development of this design of Siberian craftsmen. And although UVRK-50 was created for urban conditions, there are no restrictions for its use in cottages. What about ventilation in your country house? The article is placed in the sections: People in the process of life, whether we want it or not, emit carbon dioxide CO2 and absorb oxygen. Therefore, the influx of fresh air from the street is necessary to maintain a constant gas composition of the air in a residential building. Features of ventilation of country housesWhen a person builds a country house for himself, he seeks to do it wisely, finding the optimal ratio of price and quality. An acceptable result can be achieved by correctly designing natural ventilation. Of course, there is no question of energy efficiency here, because most of the time, except for the autumn-spring period, the outside air requires processing. In summer, the air warms up above comfortable temperature indicators, and in winter it drops much lower. The ventilation of private houses is diverse and costs completely different money. Natural ventilation or mechanical?Natural ventilation at home is the simplest, but often forgotten about it. For its implementation, it is necessary to provide a system of window ventilators or wall valves. This solution will reduce the noise coming from the street, provide the premises with the necessary amount of oxygen, and allow you to fine-tune the system. You should also remember about the natural ventilation of the kitchen, bathrooms, basements. For basements, it is necessary to provide ventilation, natural supply and exhaust ventilation. In the kitchen, be sure to make an extract from the upper zone. Another drawback of natural ventilation is the presence of drafts. The cost of natural ventilation can be 30,000-50,000 rubles per house 500-600m2 Forced country house ventilation costs more, has a more complex device, but can provide high-quality air distribution, optimal microclimate parameters. The cost of such a system for a similar house will be 300,000 rubles - 1,000,000 rubles. Design of ventilation of a country houseRegardless of the type and level of complexity of the system, the ventilation of a country house must be designed. Diteil Engneering specialists are ready to help you with choosing the best system. Thanks to the experience gained in solving the most serious problems, including for energy-efficient houses, our experts will satisfy your needs at the highest level, dear customers! |
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Drawer guides
- Design bedroom classic style wallpaper
- How to make ventilation in the apartment yourself?
- Surfboard - all about surfboards: type, size, shape
- Is it possible to carry out noise work on Sunday
- We preserve vision: the right light
- Color in the interior of the living room (50 photos): beautiful combinations
- Family horoscope for august
- Which foam rubber is better to use for a sofa
- How to choose an interior style if you like everything